Assessment of hydrogeochemistry in groundwater using water quality index model and indices approaches
- PMID: 37809741
- PMCID: PMC10558938
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19668
Assessment of hydrogeochemistry in groundwater using water quality index model and indices approaches
Abstract
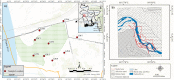
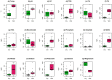
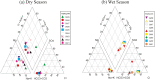
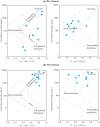
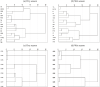
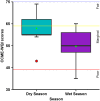
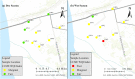
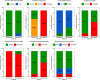
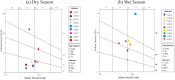
Groundwater resources around the world required periodic monitoring in order to ensure the safe and sustainable utilization for humans by keeping the good status of water quality. However, this could be a daunting task for developing countries due to the insufficient data in spatiotemporal resolution. Therefore, this research work aimed to assess groundwater quality in terms of drinking and irrigation purposes at the adjacent part of the Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant (RNPP) in Bangladesh. For the purposes of achieving the aim of this study, nine groundwater samples were collected seasonally (dry and wet season) and seventeen hydro-geochemical indicators were analyzed, including Temperature (Temp.), pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total dissolved solids (TDS), total alkalinity (TA), total hardness (TH), total organic carbon (TOC), bicarbonate (HCO3-), chloride (Cl-), phosphate (PO43-), sulfate (SO42-), nitrite (NO2-), nitrate (NO3-), sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+). The present study utilized the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment water quality index (CCME-WQI) model to assess water quality for drinking purposes. In addition, nine indices including EC, TDS, TH, sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), percent sodium (Na%), permeability index (PI), Kelley's ratio (KR), magnesium hazard ratio (MHR), soluble sodium percentage (SSP), and Residual sodium carbonate (RSC) were used in this research for assessing the water quality for irrigation purposes. The computed mean CCME-WQI score found higher during the dry season (ranges 48 to 74) than the wet season (ranges 40 to 65). Moreover, CCME-WQI model ranked groundwater quality between the "poor" and "marginal" categories during the wet season implying unsuitable water for human consumption. Like CCME-WQI model, majority of the irrigation index also demonstrated suitable water for crop cultivation during dry season. The findings of this research indicate that it requires additional care to improve the monitoring programme for protecting groundwater quality in the RNPP area. Insightful information from this study might be useful as baseline for national strategic planners in order to protect groundwater resources during the any emergencies associated with RNPP.
Keywords: CCME index; Groundwater quality; Hydrogeochemistry; Irrigation indices; Nuclear power plant; Water quality index.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Asha A.S., Saifullah A.S.M., Uddin M.G., Sheikh M.S., Uddin M.J., Diganta M.T.M. Assessment of trace metal in macroalgae and sediment of the Sundarban mangrove estuary. Appl. Water Sci. 2020;10:1–13. doi: 10.1007/s13201-019-1134-2. - DOI
-
- Kadam A., Wagh V., Patil S., Umrikar B., Sankhua R., Jacobs J. Seasonal variation in groundwater quality and beneficial use for drinking, irrigation, and industrial purposes from Deccan Basaltic Region, Western India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021;28:26082–26104. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-12115-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Osta M. El, Masoud M., Alqarawy A., Elsayed S., Gad M. vol. 14. 2022. (Groundwater Suitability for Drinking and Irrigation Using Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling in Makkah Al-Mukarramah Province, Saudi Arabia). Water (Switzerland) - DOI
-
- Uddin M.G., Moniruzzaman M., Khan M. Evaluation of groundwater quality using CCME water quality index in the Rooppur nuclear power plant area, Ishwardi, Pabna, Bangladesh. Am. J. Environ. Protect. 2017;5:33–43. doi: 10.12691/env-5-2-2. - DOI
-
- Uddin M.G., Moniruzzaman M., Quader M.A., Hasan M.A. Spatial variability in the distribution of trace metals in groundwater around the Rooppur nuclear power plant in Ishwardi, Bangladesh. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018;7:220–231. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2018.06.002. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

