Chemico-pharmacological and computational studies of Ophiorrhiza fasciculata D. Don and Psychotria silhetensis Hook. f. focusing cytotoxic, thrombolytic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties
- PMID: 37809757
- PMCID: PMC10559867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20100
Chemico-pharmacological and computational studies of Ophiorrhiza fasciculata D. Don and Psychotria silhetensis Hook. f. focusing cytotoxic, thrombolytic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties
Abstract
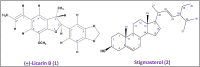
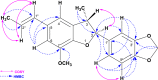
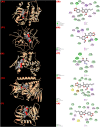
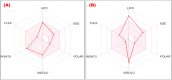
The current study sought to examine the pharmacological potentials of crude methanolic extracts of Ophiorrhiza fasciculata and Psychotria silhetensis, as well as their various solvent fractionates, with a focus on cytotoxic, thrombolytic, membrane stabilizing, antioxidant, and antibacterial activities via in vitro and in silico approaches. The extensive chromatographic and spectroscopic analyses confirmed and characterized two compounds as (±)-licarin B (1) and stigmasterol (2) from O. fasciculata and P. silhetensis, respectively. Petroleum ether soluble fraction of O. fasciculata and the aqueous soluble fraction of P. silhetensis showed the lowest 50% lethal concentrations (1.41 and 1.94 μg/mL, respectively) in brine shrimp bioassay. Likewise, petroleum ether soluble fraction of O. fasciculata and aqueous soluble fraction of P. silhetensis showed the highest thrombolytic activity with 46.66% and 50.10% lyses of the clot, respectively. The methanol and dichloromethane soluble fractions of O. fasciculata reduced erythrocyte hemolysis by 64.03% and 37.08%, respectively, under hypotonic and heat-induced conditions, compared to 81.97% and 42.12% for standard acetylsalicylic acid. In antioxidant activity test, aqueous soluble fraction O. fasciculata (IC50 = 7.22 μg/mL) revealed promising antioxidant potentialities in comparison to standard butylated hydroxytoluene (IC50 = 21.20 μg/mL). In antibacterial screening, chloroform, and dichloromethane soluble fractions of P. silhetensis showed a mild antibacterial activity compared with the standard drug ciprofloxacin. Additionally, the molecular docking study corroborated the current in vitro findings, and the isolated two constituents had higher binding affinities toward epidermal growth factor receptor, tissue plasminogen activator, vFLIP-IKK gamma stapled peptide dimer, glutathione reductase, and dihydrofolate reductase enzyme than their corresponding standard drugs. In addition, the both isolated compounds exerted favorable pharmacokinetics (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion) and toxicological profiles with drug-like qualities in computational-based ADMET and drug likeliness analyses. The current research suggests that both plants have potential as a natural treatment for treating thrombosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress. However, more thorough research is required to thoroughly screen for phytochemicals and pinpoint the precise mechanisms of action of the bioactive metabolites derived from these plants against a broad range of molecular targets.
Keywords: ADMET; Antibacterial; Antioxidant; Cytotoxicity; Drug likeliness; In silico; Membrane stabilizing; Ophiorrhiza fasciculata; Psychotria silhetensis; Thrombolytic.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

