Xuanfei Baidu decoction in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Efficacy and potential mechanisms
- PMID: 37809901
- PMCID: PMC10558324
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19163
Xuanfei Baidu decoction in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Efficacy and potential mechanisms
Abstract
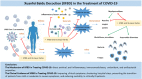
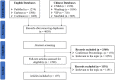
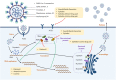
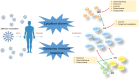
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has spread worldwide and become a major global public health concern. Although novel investigational COVID-19 antiviral candidates such as the Pfizer agent PAXLOVID™, molnupiravir, baricitinib, remdesivir, and favipiravir are currently used to treat patients with COVID-19, there is still a critical need for the development of additional treatments, as the recommended therapeutic options are frequently ineffective against SARS-CoV-2. The efficacy and safety of vaccines remain uncertain, particularly with the emergence of several variants. All 10 versions of the National Health Commission's diagnosis and treatment guidelines for COVID-19 recommend using traditional Chinese medicine. Xuanfei Baidu Decoction (XFBD) is one of the "three Chinese medicines and three Chinese prescriptions" recommended for COVID-19. This review summarizes the clinical evidence and potential mechanisms of action of XFBD for COVID-19 treatment. With XFBD, patients with COVID-19 experience improved clinical symptoms, shorter hospital stay, prevention of the progression of their symptoms from mild to moderate and severe symptoms, and reduced mortality in critically ill patients. The mechanisms of action may be associated with its direct antiviral, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, antioxidative, and antimicrobial properties. High-quality clinical and experimental studies are needed to further explore the clinical efficacy and underlying mechanisms of XFBD in COVID-19 treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chinese herbal medicine; Clinical efficacy; Mechanism; SARS-CoV-2; Xuanfei Baidu decoction.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Clinical observation of Xuanfei Baidu Decoction in treatment of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Jul;47(13):3667-3674. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220414.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35850821 Chinese.
-
Xuanfei Baidu decoction attenuates intestinal disorders by modulating NF-κB pathway, regulating T cell immunity and improving intestinal flora.Phytomedicine. 2022 Jul;101:154100. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154100. Epub 2022 Apr 17. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35489324
-
Xuanfei Baidu Decoction protects against macrophages induced inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jan 30;283:114701. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114701. Epub 2021 Oct 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34606948 Free PMC article.
-
Potential herb‒drug interactions between anti-COVID-19 drugs and traditional Chinese medicine.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Jun 5;13(9):3598-637. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.06.001. Online ahead of print. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37360014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights for infection mechanism and potential targets of COVID-19: Three Chinese patent medicines and three Chinese medicine formulas as promising therapeutic approaches.Chin Herb Med. 2023 Apr;15(2):157-168. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2022.06.014. Epub 2023 Mar 8. Chin Herb Med. 2023. PMID: 37220535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: Insight into Pathological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Benefits of Chinese Herbal Medicines.Medicines (Basel). 2024 Jul 18;11(7):14. doi: 10.3390/medicines11070014. Medicines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39051370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of the combination of BRII-196/BRII-198 in the treatment of COVID-19 vaccine breakthrough infections.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Mar 15;16(3):916-924. doi: 10.62347/NDGV1857. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38586111 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine for Viral Pneumonia Therapy: Pharmacological Basis and Mechanistic Insights.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Jan 6;21(3):989-1013. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.105086. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39897040 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Holshue M.L., DeBolt C., Lindquist S., Lofy K.H., Wiesman J., Bruce H., Spitters C., Ericson K., Wilkerson S., Tural A., Diaz G., Cohn A., Fox L., Patel A., Gerber S.I., Kim L., Tong S., Lu X., Lindstrom S., Pallansch M.A., Weldon W.C., Biggs H.M., Uyeki T.M., Pillai S.K. First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States, N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382(10):929–936. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Livingston E., Bucher K. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Italy. Jama. 2020;323(14):1335. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

