In silico and in vitro inhibition of host-based viral entry targets and cytokine storm in COVID-19 by ginsenoside compound K
- PMID: 37809955
- PMCID: PMC10558348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19341
In silico and in vitro inhibition of host-based viral entry targets and cytokine storm in COVID-19 by ginsenoside compound K
Abstract
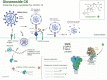
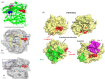
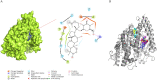
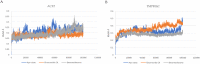
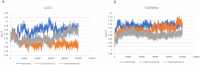
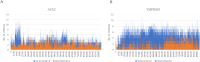
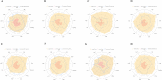
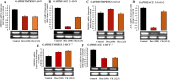
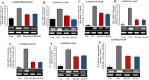
SARS-CoV-2 is a novel coronavirus that emerged as an epidemic, causing a respiratory disease with multiple severe symptoms and deadly consequences. ACE-2 and TMPRSS2 play crucial and synergistic roles in the membrane fusion and viral entry of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). The spike (S) protein of SARS-CoV-2 binds to the ACE-2 receptor for viral entry, while TMPRSS2 proteolytically cleaves the S protein into S1 and S2 subunits, promoting membrane fusion. Therefore, ACE-2 and TMPRSS2 are potential drug targets for treating COVID-19, and their inhibition is a promising strategy for treatment and prevention. This study proposes that ginsenoside compound K (G-CK), a triterpenoid saponin abundant in Panax Ginseng, a dietary and medicinal herb highly consumed in Korea and China, effectively binds to and inhibits ACE-2 and TMPRSS2 expression. We initially conducted an in-silico evaluation where G-CK showed a high affinity for the binding sites of the two target proteins of SARS-CoV-2. Additionally, we evaluated the stability of G-CK using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations for 100 ns, followed by MM-PBSA calculations. The MD simulations and free energy calculations revealed that G-CK has stable and favorable energies, leading to strong binding with the targets. Furthermore, G-CK suppressed ACE2 and TMPRSS2 mRNA expression in A549, Caco-2, and MCF7 cells at a concentration of 12.5 μg/mL and in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells at a concentration of 6.5 μg/mL, without significant cytotoxicity.ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression were significantly lower in A549 and RAW 264.7 cells following G-CK treatment. These findings suggest that G-CK may evolve as a promising therapeutic against COVID-19.
Keywords: A549; ACE-2; CaCo-2; Compound K; Ginsenoside; MCF7; Molecular docking; Molecular dynamics simulation; Raw 264.7; TMPRSS2.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

