What is the role of institutional quality in health outcomes? A panel data analysis on 158 countries from 2001-2020
- PMID: 37809989
- PMCID: PMC10560016
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20251
What is the role of institutional quality in health outcomes? A panel data analysis on 158 countries from 2001-2020
Abstract
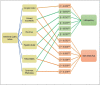
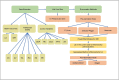
Our study investigated the impact of institutional quality on health system outcomes, utilizing worldwide governance indicators and analyzing data from 158 countries between 2001 and 2020. We employed Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to create a composite index of institutional quality and conducted various tests to select the appropriate econometric model. The role of institutional quality, along with other variables, in health outcomes was estimated using fixed effects and generalized method of moments (GMM) models. High-income and low-income countries were analyzed separately. The results of our study revealed that institutional quality, as measured by Control of Corruption, Voice and Accountability, Political Stability, Rule of Law, Regulatory Quality, and Government Effectiveness, had a negative impact on infant mortality rates and a positive impact on life expectancy. Similarly, variables such as GDP, mean years of schooling, total health expenditure, and urbanization rate showed a negative association with infant mortality rates and a positive association with life expectancy. Conversely, the logarithm of CO2 emissions exhibited a positive effect on infant mortality rates and a negative effect on life expectancy. These findings highlight the crucial role of institutional quality in determining health outcomes. Improving institutional quality contributes to the development of democratic and meritocratic systems, infrastructure enhancement, efficient tax and subsidy systems, optimal budget allocation, improved public education, and enhanced access to primary healthcare services. The influence of institutional quality is particularly significant in high-income countries compared to low-income countries. In conclusion, our study emphasizes the importance of institutional quality in shaping health system outcomes. Enhancing institutional quality is essential for the overall advancement of healthcare systems, encompassing governance, infrastructure, education, and access to healthcare services. It is crucial to prioritize efforts to improve institutional quality, especially in high-income countries, to achieve better health outcomes for populations worldwide.
Keywords: Control of corruption; Government effectiveness; Infant mortality rate; Institutional quality; Life expectancy; Regulatory quality; Rule of law.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Forum W.E. Global risk report. 2023. https://www.weforum.org/reports/global-risks-report-2023/ [Available from:
-
- Bayarsaikhan D., Tessier L., Ron A. Universal health coverage and social health protection: policy relevance to health system financing reforms. Int. Soc. Secur Rev. 2022;75(2):75–95. doi: 10.1111/issr.12295. - DOI
-
- organization wh . sustainable development goals; 2022. World Health Statistics 2022: Monitoring Health for the SDGs.https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240051157 [Available from:
-
- Erkkilä T., Piironen O. (De)politicizing good governance: the World Bank Institute, the OECD and the politics of governance indicators. Innovat. Eur. J. Soc. Sci. Res. 2014;27(4):344–360. doi: 10.1080/13511610.2013.850020. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

