Development of a Lateral-Flow Immunochromatographic Strip for the Detection of Oxytetracycline Residues in Biological Fluids
- PMID: 37810669
- PMCID: PMC10552086
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c04759
Development of a Lateral-Flow Immunochromatographic Strip for the Detection of Oxytetracycline Residues in Biological Fluids
Abstract
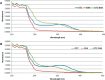
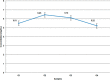
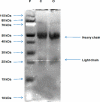
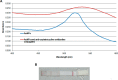
Oxytetracycline (OTC) is extensively used in veterinary medicine and for growth promotion around the globe. The indiscriminate use of OTC in food-producing animals leaves residues in animal products. The presence of these residues in animal products causes economic losses and harmful effects on consumers. Different regulatory bodies set maximum residue limits (MRLs) for different tetracyclines. To avoid harmful effects, there is a need for a simple, fast, and economical method for the screening of animal products. In this study, a fast, economical, and user-friendly lateral-flow immunochromatographic (LFIC) assay based on gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) was developed to detect the presence of OTC residues in biological fluids. AuNPs provided visual results as red lines in 6-15 min. Polyclonal rabbit IgG antibodies were produced using the immunogen of OTC. These antibodies were purified by the combined ammonium sulfate-octanoic acid precipitation method. Antibodies were conjugated to AuNPs as recognition biomolecules. A LFIC strip was optimized using borate buffer spiked with different concentrations of the OTC. The visual limit of detection (LOD) in different biological samples (milk, serum, and urine) was determined using samples spiked with OTC. The LOD was found to be 15 μg/L, which is very low from the MRL (100 μg/L) set by different regulatory authorities. This LFIC strip can be used to detect OTC residues in biological fluids for point-of-care testing (POCT). These strips are easy to use, cost-effective, and portable and provide quick results without the use of laboratory instruments.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rapid screening test for detection of oxytetracycline residues in milk using lateral flow assay.Food Chem. 2017 Mar 15;219:85-92. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.09.090. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 27765263
-
Development of a quantum dot-based immunochromatography test strip for rapid screening of oxytetracycline and 4-epi-oxytetracycline in edible animal tissues.Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2017 Mar;34(3):371-378. doi: 10.1080/19440049.2016.1277038. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2017. PMID: 28110635
-
Visual and fluorometric lateral flow immunoassay combined with a dual-functional test mode for rapid determination of tetracycline antibiotics.Mikrochim Acta. 2018 Aug 7;185(9):404. doi: 10.1007/s00604-018-2945-9. Mikrochim Acta. 2018. PMID: 30088104
-
Fluorescent Ru(phen)3(2+)-doped silica nanoparticles-based ICTS sensor for quantitative detection of enrofloxacin residues in chicken meat.Anal Chem. 2013 May 21;85(10):5120-8. doi: 10.1021/ac400502v. Epub 2013 May 7. Anal Chem. 2013. PMID: 23614687
-
A Novel Lateral Flow Immunochromatographic Assay for Rapid and Simultaneous Detection of Aflatoxin B1 and Zearalenone in Food and Feed Samples Based on Highly Sensitive and Specific Monoclonal Antibodies.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Sep 2;14(9):615. doi: 10.3390/toxins14090615. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36136553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crescenzo G.; Tinelli A.; Centoducati G.; Zizzadoro C.; Leone R.; Piccinno M.; Lai O. Residue depletion and histopathological alterations in gilthead sea bream (Sparusaurata) after oral administration of oxytetracycline. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2021, 49, 167–175. 10.1080/09712119.2021.1921779. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

