Deep Proteomic Compound Profiling with the Orbitrap Ascend Tribrid Mass Spectrometer Using Tandem Mass Tags and Real-Time Search
- PMID: 37811788
- PMCID: PMC10785648
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c01701
Deep Proteomic Compound Profiling with the Orbitrap Ascend Tribrid Mass Spectrometer Using Tandem Mass Tags and Real-Time Search
Abstract
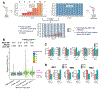
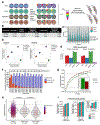
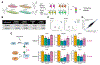
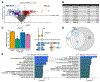
Tandem mass tags (TMT) and tribrid mass spectrometers are a powerful combination for high-throughput proteomics with high quantitative accuracy. Increasingly, this technology is being used to map the effects of drugs on the proteome. However, the depth of proteomic profiling is still limited by sensitivity and speed. The new Orbitrap Ascend mass spectrometer was designed to address these limitations with a combination of hardware and software improvements. We evaluated the performance of the Ascend in multiple contexts including deep proteomic profiling. We found that the Ascend exhibited increased sensitivity, yielding higher signal-to-noise ratios than the Orbitrap Eclipse with shorter injection times. As a result, higher numbers of peptides and proteins were identified and quantified, especially with low sample input. TMT measurements had significantly improved signal-to-noise ratios, improving quantitative precision. In a fractionated 16plex sample that profiled proteomic differences across four human cell lines, the Ascend was able to quantify hundreds more proteins than the Eclipse, many of them low-abundant proteins, and the Ascend was able to quantify >8000 proteins in 30% less instrument time. We used the Ascend to analyze 8881 proteins in HCT116 cancer cells treated with covalent sulfolane/sulfolene inhibitors of peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 (PIN1), a phosphorylation-specific peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase implicated in several cancers. We characterized these PIN1 inhibitors' effects on the proteome and identified discrepancies among the different compounds, which will facilitate a better understanding of the structure-activity relationship of this class of compounds. The Ascend was able to quantify statistically significant, potentially therapeutically relevant changes in proteins that the Eclipse could not detect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): G.C.M., W.D.B., J.D.C., D.B., J.H., R.H., and V.Z. are employees of Thermo Fisher Scientific, the manufacturer of the Orbitrap Ascend Tribrid mass spectrometer.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

