Major data analysis errors invalidate cancer microbiome findings
- PMID: 37811944
- PMCID: PMC10653788
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.01607-23
Major data analysis errors invalidate cancer microbiome findings
Abstract
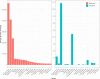
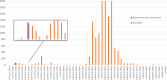
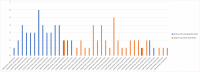
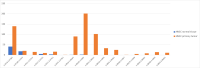
Recent reports showing that human cancers have a distinctive microbiome have led to a flurry of papers describing microbial signatures of different cancer types. Many of these reports are based on flawed data that, upon re-analysis, completely overturns the original findings. The re-analysis conducted here shows that most of the microbes originally reported as associated with cancer were not present at all in the samples. The original report of a cancer microbiome and more than a dozen follow-up studies are, therefore, likely to be invalid.
Keywords: bioinformatics; cancer; computational biology; metagenomics; microbiome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Update of
-
Major data analysis errors invalidate cancer microbiome findings.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 31:2023.07.28.550993. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.28.550993. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: mBio. 2023 Oct 31;14(5):e0160723. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01607-23. PMID: 37577699 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Poore GD, Kopylova E, Zhu Q, Carpenter C, Fraraccio S, Wandro S, Kosciolek T, Janssen S, Metcalf J, Song SJ, Kanbar J, Miller-Montgomery S, Heaton R, Mckay R, Patel SP, Swafford AD, Knight R. 2020. Microbiome analyses of blood and tissues suggest cancer diagnostic approach. Nat 579:567–574. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2095-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

