Fn14 promotes myoblast fusion during regenerative myogenesis
- PMID: 37813488
- PMCID: PMC10561765
- DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202302312
Fn14 promotes myoblast fusion during regenerative myogenesis
Abstract
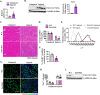
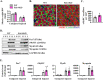
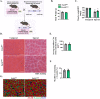
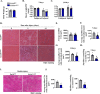
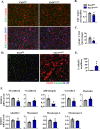
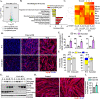
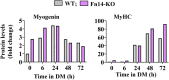
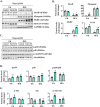
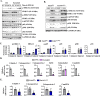
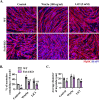
Skeletal muscle regeneration involves coordinated activation of an array of signaling pathways. Fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 (Fn14) is a bona fide receptor for the TWEAK cytokine. Levels of Fn14 are increased in the skeletal muscle of mice after injury. However, the cell-autonomous role of Fn14 in muscle regeneration remains unknown. Here, we demonstrate that global deletion of the Fn14 receptor in mice attenuates muscle regeneration. Conditional ablation of Fn14 in myoblasts but not in differentiated myofibers of mice inhibits skeletal muscle regeneration. Fn14 promotes myoblast fusion without affecting the levels of myogenic regulatory factors in the regenerating muscle. Fn14 deletion in myoblasts hastens initial differentiation but impairs their fusion. The overexpression of Fn14 in myoblasts results in the formation of myotubes having an increased diameter after induction of differentiation. Ablation of Fn14 also reduces the levels of various components of canonical Wnt and calcium signaling both in vitro and in vivo. Forced activation of Wnt signaling rescues fusion defects in Fn14-deficient myoblast cultures. Collectively, our results demonstrate that Fn14-mediated signaling positively regulates myoblast fusion and skeletal muscle regeneration.
© 2023 Tomaz da Silva et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Methodological) 57: 289–300. 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
