Targeting pancreatic cancer metabolic dependencies through glutamine antagonism
- PMID: 37814010
- PMCID: PMC10824664
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-023-00647-3
Targeting pancreatic cancer metabolic dependencies through glutamine antagonism
Abstract
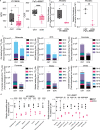
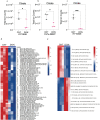
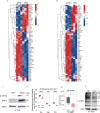
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells use glutamine (Gln) to support proliferation and redox balance. Early attempts to inhibit Gln metabolism using glutaminase inhibitors resulted in rapid metabolic reprogramming and therapeutic resistance. Here, we demonstrated that treating PDAC cells with a Gln antagonist, 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine (DON), led to a metabolic crisis in vitro. In addition, we observed a profound decrease in tumor growth in several in vivo models using sirpiglenastat (DRP-104), a pro-drug version of DON that was designed to circumvent DON-associated toxicity. We found that extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling is increased as a compensatory mechanism. Combinatorial treatment with DRP-104 and trametinib led to a significant increase in survival in a syngeneic model of PDAC. These proof-of-concept studies suggested that broadly targeting Gln metabolism could provide a therapeutic avenue for PDAC. The combination with an ERK signaling pathway inhibitor could further improve the therapeutic outcome.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04471415.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.C.K. has financial interests in Vescor Therapeutics and is an inventor on patents pertaining to KRAS-regulated metabolic pathways and redox control pathways in pancreatic cancer, targeting GOT1 as a therapeutic approach, targeting alanine transport, and the autophagic control of iron metabolism. A.C.K. is on the scientific advisory board of Rafael/Cornerstone Pharmaceuticals and OncoRev, and has been a consultant for Deciphera and Abbvie. R.W. and Y.Y. are employees and have an ownership interest in Dracen Pharmaceuticals. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures













References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

