Sacral neuromodulation in endometriosis - A promising treatment option for chronic pelvic pain
- PMID: 37814355
- PMCID: PMC10619602
- DOI: 10.1111/aogs.14690
Sacral neuromodulation in endometriosis - A promising treatment option for chronic pelvic pain
Abstract
Introduction: Chronic pelvic pain (CPP) affects over one fifth of women worldwide, and endometriosis is one of the most common causes. In the present study, we examined whether sacral neuromodulation (SNM) is effective in the treatment of refractory chronic pelvic pain in women with endometriosis.
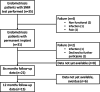
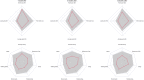
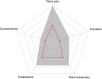
Material and methods: This multicenter prospective pilot study was started in 2017 and includes patients with chronic pelvic pain with no other obvious pathology than endometriosis. Other treatment options have been tried or they are unsuitable. Patients underwent SNM implantation. The main outcome was postoperative pain reduction and secondary outcome was quality of life. The following questionnaires were used to assess the outcomes: Brief pain inventory (BPI), clinical global impression - improvement (CGI-I), 15D-measure of health-related quality of life, and Biberoglu and Behrman (B&B) score.
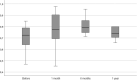
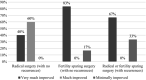
Results: A total of 35 patients underwent the SNM procedure and, at the time of analysis, 15 patients had returned one-year questionnaires. The patients had a history of endometriosis for a median of 5.5 (interquartile range 2-9) years, with no correlation between the severity of symptoms and the duration of the disease (p = 0.158). A total of 31 patients (89%) were implanted with the internal pulse generator. There were statistically significant changes in BPI pain-related items. Worst experienced daily pain decreased among those who returned 12-month questionnaires from median 9 to 5 (p = 0.006), average daily pain from 6 to 3.5 (p = 0.004), and least daily pain from 3 to 1 (p = 0.004). Based on the CGI questionnaire (n = 14), at 12 months nine patients (60%) experienced great improvement in their symptoms, three patients (20%) much improvement and two patients (13%) minimal improvement. None of the patients experienced worsening of their symptoms. There was a statistically significant change in overall 15D score at 1 month (p < 0.001), 6 months (p = 0.001) and 12 months (p = 0.018), when the results were compared to baseline values. Median B&B score also improved significantly and decreased from a baseline value of 8 (4-12) to 4.5 (0-6), p = 0.002.
Conclusions: Based on the preliminary findings of our study, SNM might be a promising treatment of CPP in endometriosis patients.
Keywords: chronic pain; endometriosis; pelvic pain; sacral neuromodulation.
© 2023 The Authors. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology (NFOG).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Peters AA, van Dorst E, Jellis B, van Zuuren E, Hermans J, Trimbos JB. A randomized clinical trial to compare two different approaches in women with chronic pelvic pain. Obstet Gynecol. 1991;77(5):740‐744. - PubMed
-
- Mounsey AL, Wilgus A, Slawson DC. Diagnosis and management of endometriosis. Am Fam Physician. 2006;74(4):594‐600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

