Decarboxylation and Tandem Reduction/Decarboxylation Pathways to Substituted Phenols from Aromatic Carboxylic Acids Using Bimetallic Nanoparticles on Supported Ionic Liquid Phases as Multifunctional Catalysts
- PMID: 37815193
- PMCID: PMC10591467
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c09290
Decarboxylation and Tandem Reduction/Decarboxylation Pathways to Substituted Phenols from Aromatic Carboxylic Acids Using Bimetallic Nanoparticles on Supported Ionic Liquid Phases as Multifunctional Catalysts
Abstract
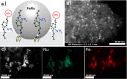
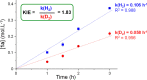
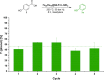
Valuable substituted phenols are accessible via the selective decarboxylation of hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives using multifunctional catalysts composed of bimetallic iron-ruthenium nanoparticles immobilized on an amine-functionalized supported ionic liquid phase (Fe25Ru75@SILP+IL-NEt2). The individual components of the catalytic system are assembled using a molecular approach to bring metal and amine sites into close contact on the support material, providing high stability and high decarboxylation activity. Operating under a hydrogen atmosphere was found to be essential to achieve high selectivity and yields. As the catalyst materials enable also the selective hydrogenation and hydrodeoxygenation of various additional functional groups (i.e., formyl, acyl, and nitro substituents), direct access to the corresponding phenols can be achieved via integrated tandem reactions. The approach opens versatile synthetic pathways for the production of valuable phenols from a wide range of readily available substrates, including compounds derived from lignocellulosic biomass.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hutchins R. O.; Hutchins M. K.; Fleming I.. Comprehensive Organic Synthesis; Elsevier: 1991.
-
- Lorenc F.; Lambeth G.; Scheffer W.. Alkylphenols; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: 2003.
-
- Fiege H.; Voges H.-W.; Hamamoto T.; Umemura S.; Iwata T.; Miki H.; Fujita Y.; Buysch H.-J.; Garbe D.; Paulus W. Phenol Derivatives. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2012, 503–519. 10.1002/14356007.a19_313. - DOI
-
- Liu Y.; Baráth E.; Shi H.; Hu J.; Camaioni D. M.; Lercher J. A. Solvent-Determined Mechanistic Pathways in Zeolite-H-BEA-Catalysed Phenol Alkylation. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 141–147. 10.1038/s41929-017-0015-z. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

