Disruption of Dopamine Homeostasis Associated with Alteration of Proteins in Synaptic Vesicles: A Putative Central Mechanism of Parkinson's Disease Pathogenesis
- PMID: 37815908
- PMCID: PMC11081171
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2023.0821-2
Disruption of Dopamine Homeostasis Associated with Alteration of Proteins in Synaptic Vesicles: A Putative Central Mechanism of Parkinson's Disease Pathogenesis
Abstract
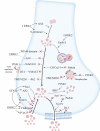
Vestigial dopaminergic cells in PD have selectivity for a sub-class of hypersensitive neurons with the nigrostriatal dopamine (DA) tract. DA is modulated in pre-synaptic nerve terminals to remain stable. To be specific, proteins at DA release sites that have a function of synthesizing and packing DA in cytoplasm, modulating release and reingestion, and changing excitability of neurons, display regional discrepancies that uncover relevancy of the observed sensitivity to neurodegenerative changes. Although the reasons of a majority of PD cases are still indistinct, heredity and environment are known to us to make significant influences. For decades, genetic analysis of PD patients with heredity in family have promoted our comprehension of pathogenesis to a great extent, which reveals correlative mechanisms including oxidative stress, abnormal protein homeostasis and mitochondrial dysfunction. In this review, we review the constitution of presynaptic vesicle related to DA homeostasis and describe the genetic and environmental evidence of presynaptic dysfunction that increase risky possibility of PD concerning intracellular vesicle transmission and their functional outcomes. We summarize alterations in synaptic vesicular proteins with great involvement in the reasons of some DA neurons highly vulnerable to neurodegenerative changes. We generalize different potential targets and therapeutic strategies for different pathogenic mechanisms, providing a reference for further studies of PD treatment in the future. But it remains to be further researched on this recently discovered and converging mechanism of vesicular dynamics and PD, which will provide a more profound comprehension and put up with new therapeutic tactics for PD patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Barnett R (2016). Parkinson's disease. Lancet, 387:217. - PubMed
-
- Lazzeri G, Lenzi P, Busceti CL, Ferrucci M, Falleni A, Bruno V, et al. (2007). Mechanisms involved in the formation of dopamine-induced intracellular bodies within striatal neurons. J Neurochem, 101:1414-1427. - PubMed
-
- Pasquali L, Lazzeri G, Isidoro C, Ruggieri S, Paparelli A, Fornai F (2008). Role of autophagy during methamphetamine neurotoxicity. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 1139:191-196. - PubMed
-
- Sossi V, de la Fuente-Fernandez R, Nandhagopal R, Schulzer M, McKenzie J, Ruth TJ, et al. (2010). Dopamine turnover increases in asymptomatic LRRK2 mutations carriers. Mov Disord, 25:2717-2723. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical