Angiotensin II-mediated hippocampal hypoperfusion and vascular dysfunction contribute to vascular cognitive impairment in aged hypertensive rats
- PMID: 37817376
- PMCID: PMC10917018
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.13491
Angiotensin II-mediated hippocampal hypoperfusion and vascular dysfunction contribute to vascular cognitive impairment in aged hypertensive rats
Abstract
Introduction: Chronic hypertension increases the risk of vascular cognitive impairment (VCI) by ∼60%; however, how hypertension affects the vasculature of the hippocampus remains unclear but could contribute to VCI.
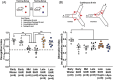
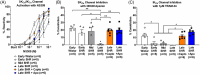
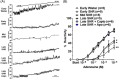
Methods: Memory, hippocampal perfusion, and hippocampal arteriole (HA) function were investigated in male Wistar rats or spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) in early (4 to 5 months old), mid (8 to 9 months old), or late adulthood (14 to 15 months old). SHR in late adulthood were chronically treated with captopril (angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor) or apocynin (antioxidant) to investigate the mechanisms by which hypertension contributes to VCI.
Results: Impaired memory in SHR in late adulthood was associated with HA endothelial dysfunction, hyperconstriction, and ∼50% reduction in hippocampal blood flow. Captopril, but not apocynin, improved HA function, restored perfusion, and rescued memory function in aged SHR.
Discussion: Hippocampal vascular dysfunction contributes to hypertension-induced memory decline through angiotensin II signaling, highlighting the therapeutic potential of HAs in protecting neurocognitive health later in life.
Highlights: Vascular dysfunction in the hippocampus contributes to vascular cognitive impairment. Memory declines with age during chronic hypertension. Angiotensin II causes endothelial dysfunction in the hippocampus in hypertension. Angiotensin II-mediated hippocampal arteriole dysfunction reduces blood flow. Vascular dysfunction in the hippocampus impairs perfusion and memory function.
Keywords: aging; angiotensin II; chronic hypertension; hippocampus; vascular cognitive impairment; vascular dementia.
© 2023 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare (supporting information).
Figures



References
-
- WHO . Global status report on the public health response to dementia. World Health Organization; 2021.
-
- 2022 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2022;18:700‐789 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

