Impact of alternating amino acid sequences on beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 37819792
- PMCID: PMC10599720
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.205095
Impact of alternating amino acid sequences on beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
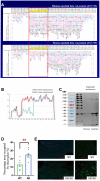
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a chronic neurodegenerative disease and the common cause of dementia. The aggregation of beta-amyloid (Aβ peptide) leading to excessive neuroinflammation is considered to be the neuropathological hallmark of AD, although the precise mechanisms remain unclear. Oligomerization of these peptides may be associated with their 42 amino acid residue arrangement. However, the process of amyloid plaque formation is still not well known. The protein folding-shape code (PFSC) method is a powerful tool to analyze protein confirmation which could exhibit the local structural folding features in detail. In our study, we utilized the PFSC to analyze Aβ peptide in humans and mice and found that mouse Aβ42 is less likely to polymerize than human's. Subsequently, we used the PFSC method to analyze the 42 amino acids of Aβ, transformed some species in human Aβ42 and obtained 7 mutants. We showed that it was not easy to aggregate Aβ in mutants. Herein, inflammatory responses were decreased, as indicated by the expression of cytokines. We confirmed that the neurotoxicity of mutant human Aβ was decreased by preventing peptide aggregation. This may represent a new therapeutic approach for treating AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; alternating amino; beta-amyloid; neuroinflammation; neurotoxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Jack CR Jr, Knopman DS, Jagust WJ, Petersen RC, Weiner MW, Aisen PS, Shaw LM, Vemuri P, Wiste HJ, Weigand SD, Lesnick TG, Pankratz VS, Donohue MC, Trojanowski JQ. Tracking pathophysiological processes in Alzheimer's disease: an updated hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers. Lancet Neurol. 2013; 12:207–16. 10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70291-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

