m6A-Modified circTET2 Interacting with HNRNPC Regulates Fatty Acid Oxidation to Promote the Proliferation of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
- PMID: 37821382
- PMCID: PMC10700176
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202304895
m6A-Modified circTET2 Interacting with HNRNPC Regulates Fatty Acid Oxidation to Promote the Proliferation of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
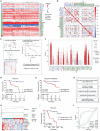
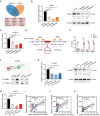
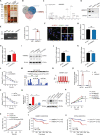
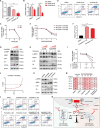
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a hematological malignancy with high metabolic heterogeneity. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification plays an important role in metabolism through regulating circular RNAs (circRNAs). However, the underlying mechanism is not yet fully understood in CLL. Herein, an m6A scoring system and an m6A-related circRNA prognostic signature are established, and circTET2 as a potential prognostic biomarker for CLL is identified. The level of m6A modification is found to affect the transport of circTET2 out of the nucleus. By interacting with the RNA-binding protein (RBP) heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (HNRNPC), circTET2 regulates the stability of CPT1A and participates in the lipid metabolism and proliferation of CLL cells through mTORC1 signaling pathway. The mTOR inhibitor dactolisib and FAO inhibitor perhexiline exert a synergistic effect on CLL cells. In addition, the biogenesis of circTET2 can be affected by the splicing process and the RBPs RBMX and YTHDC1. CP028, a splicing inhibitor, modulates the expression of circTET2 and shows pronounced inhibitory effects. In summary, circTET2 plays an important role in the modulation of lipid metabolism and cell proliferation in CLL. This study demonstrates the clinical value of circTET2 as a prognostic indicator as well as provides novel insights in targeting treatment for CLL.
Keywords: HNRNPC; N6-methyladenosine (m6A); chronic lymphocytic leukemia; circTET2; circular RNA; fatty acid oxidation; proliferation.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- a) Ito H., Nakamae I., Kato J. Y., Yoneda‐Kato N., J. Clin. Invest. 2021, 131, 141529; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Subedi A., Liu Q., Ayyathan D. M., Sharon D., Cathelin S., Hosseini M., Xu C., Voisin V., Bader G. D., D'Alessandro A., Lechman E. R., Dick J. E., Minden M. D., Wang J. C. Y., Chan S. M., Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 1851; - PubMed
- c) Galicia‐Vázquez G., Aloyz R., Front Oncol 2018, 8, 411. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kristensen L. S., Jakobsen T., Hager H., Kjems J., Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2022, 19, 188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82200213/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81970146/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82170185/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- ZDXK202209/Jiangsu Province Capability Improvement Project through Science, Technology and Education
- BK20211376/the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
