PTPN23 ubiquitination by WDR4 suppresses EGFR and c-MET degradation to define a lung cancer therapeutic target
- PMID: 37821451
- PMCID: PMC10567730
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-06201-4
PTPN23 ubiquitination by WDR4 suppresses EGFR and c-MET degradation to define a lung cancer therapeutic target
Erratum in
-
Correction: PTPN23 ubiquitination by WDR4 suppresses EGFR and c-MET degradation to define a lung cancer therapeutic target.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jul 2;15(7):468. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06747-x. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38956428 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
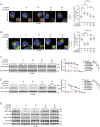
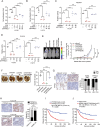
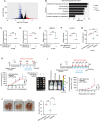
Aberrant overexpression or activation of EGFR drives the development of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) by secondary EGFR mutations or c-MET amplification/activation remains as a major hurdle for NSCLC treatment. We previously identified WDR4 as a substrate adaptor of Cullin 4 ubiquitin ligase and an association of WDR4 high expression with poor prognosis of lung cancer. Here, using an unbiased ubiquitylome analysis, we uncover PTPN23, a component of the ESCRT complex, as a substrate of WDR4-based ubiquitin ligase. WDR4-mediated PTPN23 ubiquitination leads to its proteasomal degradation, thereby suppressing lysosome trafficking and degradation of wild type EGFR, EGFR mutant, and c-MET. Through this mechanism, WDR4 sustains EGFR and c-MET signaling to promote NSCLC proliferation, migration, invasion, stemness, and metastasis. Clinically, PTPN23 is downregulated in lung cancer and its low expression correlates with WDR4 high expression and poor prognosis. Targeting WDR4-mediated PTPN23 ubiquitination by a peptide that competes with PTPN23 for binding WDR4 promotes EGFR and c-MET degradation to block the growth and progression of EGFR TKI-resistant NSCLC. These findings identify a central role of WDR4/PTPN23 axis in EGFR and c-MET trafficking and a potential therapeutic target for treating EGFR TKI-resistant NSCLC.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Endothelial PAS domain-containing protein 1 confers TKI-resistance by mediating EGFR and MET pathways in non-small cell lung cancer cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(4):549-57. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1016689. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25831463 Free PMC article.
-
Leukocyte Cell-Derived Chemotaxin 2 Retards Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression Through Antagonizing MET and EGFR Activities.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(1):337-355. doi: 10.1159/000495233. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30453282
-
MET and AXL inhibitor NPS-1034 exerts efficacy against lung cancer cells resistant to EGFR kinase inhibitors because of MET or AXL activation.Cancer Res. 2014 Jan 1;74(1):253-62. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1103. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24165158
-
Current mechanism of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and updated therapy strategies in human nonsmall cell lung cancer.J Cancer Res Ther. 2016 Dec;12(Supplement):C131-C137. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.200613. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 28230005 Review.
-
Strategies to overcome acquired resistance to EGFR TKI in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2019 Oct;21(10):1287-1301. doi: 10.1007/s12094-019-02075-1. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30864018 Review.
Cited by
-
N7-methylguanosine modification in cancers: from mechanisms to therapeutic potential.J Hematol Oncol. 2025 Jan 29;18(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s13045-025-01665-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39881381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive multi-omics analysis reveals the prognostic and immune regulatory characteristics of the PTPN family in osteosarcoma.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 26;20(6):e0326872. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326872. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40570022 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potentials of Ubiquitin-Proteasome System in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cell Prolif. 2025 Jul;58(7):e70050. doi: 10.1111/cpr.70050. Epub 2025 May 1. Cell Prolif. 2025. PMID: 40313038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generative modeling for RNA splicing predictions and design.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 24:2025.01.20.633986. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.20.633986. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39896553 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Role of Epiregulin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis as a Mediator via EGFR Signaling in the Cancer Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 17;25(8):4405. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084405. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:121–8. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70364-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

