Treatment with trastuzumab deruxtecan in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer and brain metastases and/or leptomeningeal disease (ROSET-BM)
- PMID: 37821514
- PMCID: PMC10567705
- DOI: 10.1038/s41523-023-00584-5
Treatment with trastuzumab deruxtecan in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer and brain metastases and/or leptomeningeal disease (ROSET-BM)
Abstract
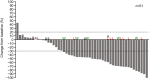
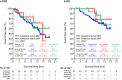
Therapeutic options for breast cancer patients with brain metastases (BM)/leptomeningeal carcinomatosis (LMC) are limited. Here, we report on the effectiveness and safety of trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer patients with BM. Data were analyzed for 104 patients administered T-DXd. Overall response rate (ORR), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), intracranial (IC)-ORR, and IC-PFS were evaluated. ORR by investigator assessment was 55.7% (total population). Median PFS was 16.1 months; 12-month OS rate was 74.9% (total population). Median time-to-treatment failure was 9.7 months. In 51 patients with BM imaging, IC-ORR and median IC-PFS by independent central review were 62.7% and 16.1 months, respectively. In 19 LMC patients, 12-month PFS and OS rates were 60.7% and 87.1%, respectively. T-DXd showed effectiveness regarding IC-ORR, IC-PFS, PFS, and OS in breast cancer patients with BM/active BM, and sustained systemic and central nervous system disease control in LMC patients.Trial Registration: UMIN000044995.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
N.N. reports consulting or advisory roles for AstraZeneca K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd; and has received lecture fees from AstraZeneca K.K., Eisai Co., Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., and Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd; and research funding from Pfizer Japan Inc., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., and Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd. T.Y. has received lecture fees from AstraZeneca K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., and Pfizer Japan Inc. K.I. has received research funding from Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., AstraZeneca K.K., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., MSD K.K., and Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. MYamaguchi has received speakers’ bureau from Pfizer Japan Inc., Novartis Pharma K.K., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., MEDICON Co., Ltd., Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd. TA has received speakers’ bureau from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., and AstraZeneca K.K. N.S. reports consulting or advisory roles for Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., and Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd; and has received speakers’ bureau from Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., Eisai Co., Ltd., Yakult Honsha Co., Ltd., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., AstraZeneca K.K., Merck Biopharma Co., Ltd., Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Nippon Kayaku Co., Ltd.; and research funding from Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and MSD K.K. JT reports consulting or advisory roles for Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., AstraZeneca K.K., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., and Seagen Inc.; and has received speakers’ bureau from Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., and Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd.; and research funding from Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., AstraZeneca K.K., Eisai Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Seagen Inc., Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., Sant Joan de Déu Research Foundation, and West Japan Oncology Group. YK, TI, and KShiosakai are employees of Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd. H.N., K. Shiraishi, H.K., M. Yamamoto, K.M., S.T., S.K., A.S., Y.O., and S.S. have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

