Design and testing of a humanized porcine donor for xenotransplantation
- PMID: 37821590
- PMCID: PMC10567564
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06594-4
Design and testing of a humanized porcine donor for xenotransplantation
Abstract
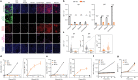
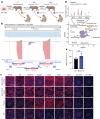
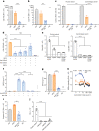
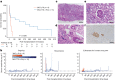
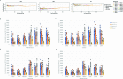
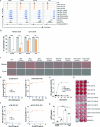
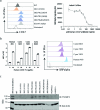
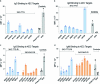
Recent human decedent model studies1,2 and compassionate xenograft use3 have explored the promise of porcine organs for human transplantation. To proceed to human studies, a clinically ready porcine donor must be engineered and its xenograft successfully tested in nonhuman primates. Here we describe the design, creation and long-term life-supporting function of kidney grafts from a genetically engineered porcine donor transplanted into a cynomolgus monkey model. The porcine donor was engineered to carry 69 genomic edits, eliminating glycan antigens, overexpressing human transgenes and inactivating porcine endogenous retroviruses. In vitro functional analyses showed that the edited kidney endothelial cells modulated inflammation to an extent that was indistinguishable from that of human endothelial cells, suggesting that these edited cells acquired a high level of human immune compatibility. When transplanted into cynomolgus monkeys, the kidneys with three glycan antigen knockouts alone experienced poor graft survival, whereas those with glycan antigen knockouts and human transgene expression demonstrated significantly longer survival time, suggesting the benefit of human transgene expression in vivo. These results show that preclinical studies of renal xenotransplantation could be successfully conducted in nonhuman primates and bring us closer to clinical trials of genetically engineered porcine renal grafts.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
eGenesis has filed multiple patent applications covering the subject matter of this paper. R.P.A., J.V.L., D.H., A.A., D.A.-A, J.C.C., S. Chhangawala, R.J.E., N.E., K.G., A.K.G., X.G., K.C.H., P.H., S.H., N.H., L.A.K., Y.K., T.L., F.L., M.L., S.C.L., C.N., M.P., V.B.P., R.A.P., R.P., L.P., L.Q., W.T.S., D. Stevens, K.S., O.D.S., Y.X., S.Y., G.E.Z., M.C., M.E.Y. and W.Q. contributed to this work as employees of eGenesis and may have an equity interest, in the form of stock options, in eGenesis. J.N.C. and X.T. contributed to this work as employees of eGenesis. D.J.F. was partially supported by eGenesis. R.B.C., D.J.F., T.K. and G.L. are consultants for eGenesis. J.F.M. serves on the eGenesis Scientific Advisory Board. G.M.C. is co-founder and scientific advisor to eGenesis.
Figures




Comment in
-
Pig-to-primate organ transplants require genetic modifications of donor.Nature. 2023 Oct;622(7982):244-245. doi: 10.1038/d41586-023-02817-w. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37821585 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

