A nomogram based on the expression level of angiopoietin-like 4 to predict the severity of community-acquired pneumonia
- PMID: 37821811
- PMCID: PMC10568757
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-023-08648-4
A nomogram based on the expression level of angiopoietin-like 4 to predict the severity of community-acquired pneumonia
Abstract
Background: The morbidity and mortality of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) remain high among infectious diseases. It was reported that angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4) could be a diagnostic biomarker and a therapeutic target for pneumonia. This study aimed to develop a more objective, specific, accurate, and individualized scoring system to predict the severity of CAP.
Methods: Totally, 31 non-severe community-acquired pneumonia (nsCAP) patients and 14 severe community-acquired pneumonia (sCAP) patients were enrolled in this study. The CURB-65 and pneumonia severity index (PSI) scores were calculated from the clinical data. Serum ANGPTL4 level was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). After screening factors by univariate analysis and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, multivariate logistic regression analysis of ANGPTL4 expression level and other risk factors was performed, and a nomogram was developed to predict the severity of CAP. This nomogram was further internally validated by bootstrap resampling with 1000 replications through the area under the ROC curve (AUC), the calibration curve, and the decision curve analysis (DCA). Finally, the prediction performance of the new nomogram model, CURB-65 score, and PSI score was compared by AUC, net reclassification index (NRI), and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI).
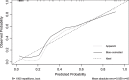
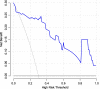
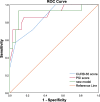
Results: A nomogram for predicting the severity of CAP was developed using three factors (C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), and ANGPTL4). According to the internal validation, the nomogram showed a great discrimination capability with an AUC of 0.910. The Hosmer-Lemeshow test and the approximately fitting calibration curve suggested a satisfactory accuracy of prediction. The results of DCA exhibited a great net benefit. The AUC values of CURB-65 score, PSI score, and the new prediction model were 0.857, 0.912, and 0.940, respectively. NRI comparing the new model with CURB-65 score was found to be statistically significant (NRI = 0.834, P < 0.05).
Conclusion: A robust model for predicting the severity of CAP was developed based on the serum ANGPTL4 level. This may provide new insights into accurate assessment of the severity of CAP and its targeted therapy, particularly in the early-stage of the disease.
Keywords: Angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4); Biomarker; Precision medicine; Prediction model; Severe community-acquired pneumonia.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Construction and verification of a nomogram prediction model of severe adult community-acquired pneumonia].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022 Sep;34(9):935-940. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220720-00678. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022. PMID: 36377447 Chinese.
-
Nomogram Prediction Model of the Severity of CAP Patients Based on Blood Indicators.Clin Lab. 2023 Feb 1;69(2). doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2022.220405. Clin Lab. 2023. PMID: 36787556
-
Risk stratification and prediction value of procalcitonin and clinical severity scores for community-acquired pneumonia in ED.Am J Emerg Med. 2018 Dec;36(12):2155-2160. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2018.03.050. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Am J Emerg Med. 2018. PMID: 29691103
-
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting the risk of nursing home-acquired pneumonia.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Nov;26(22):8276-8288. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202211_30360. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36459011 Review.
-
Utility of pneumonia severity assessment tools for mortality prediction in healthcare-associated pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 5;14(1):12964. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63618-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38839837 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
ANGPTL4-the Link Binding Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(15):2931-2949. doi: 10.2174/0109298673320024240829070906. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39252623 Review.
-
Adipose Factor ANGPTL4: Its Role in Aging Mechanisms and Associated Diseases.Clin Interv Aging. 2025 Jun 28;20:911-929. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S522049. eCollection 2025. Clin Interv Aging. 2025. PMID: 40606512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated Plasma Angiopoietin-like 4 Protein Levels in Adult Patients with Dengue.Viruses. 2025 Feb 6;17(2):226. doi: 10.3390/v17020226. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40006981 Free PMC article.
-
An explainable machine learning-based model to predict intensive care unit admission among patients with community-acquired pneumonia and connective tissue disease.Respir Res. 2024 Jun 18;25(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02874-3. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 38890628 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of CDKN2A in cuproptosis through defining cuproptosis-related gene signature in ovarian cancer.J Cancer. 2025 Jul 24;16(11):3355-3371. doi: 10.7150/jca.115374. eCollection 2025. J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40861807 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2019A1515110787/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2020A1515110973/Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province
- A2020176/Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province of China
- ZH2202200012HJL/Zhuhai Science and Technology Planning Project for medicine of Zhuhai City
- B2019033/Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

