Quality of Life in Patients with High-grade Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer Undergoing Standard Versus Reduced Frequency of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Instillations: The EAU-RF NIMBUS Trial
- PMID: 37822514
- PMCID: PMC10562176
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euros.2023.08.004
Quality of Life in Patients with High-grade Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer Undergoing Standard Versus Reduced Frequency of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Instillations: The EAU-RF NIMBUS Trial
Abstract
Background: Adverse events induced by intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) to treat high-grade non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) often lead to treatment discontinuation. The EAU-RF NIMBUS trial found a reduced number of standard-dose BCG instillations to be inferior with the standard regimen. Nonetheless, it remains important to evaluate whether patients in the reduced BCG treatment arm had better quality of life (QoL) due to a possible reduction in toxicity or burden.
Objective: To evaluate whether patients in the EAU-RF NIMBUS trial experienced better QoL after a reduced BCG instillation frequency.
Design setting and participants: A total of 359 patients from 51 European sites were randomized to one of two treatment arms between December 2013 and July 2019. The standard frequency arm (n = 182) was 6 weeks of BCG induction followed by 3 weeks of maintenance at months 3, 6, and 12. The reduced frequency arm (n = 177) was BCG induction at weeks 1, 2, and 6, followed by maintenance instillations at weeks 1 and 3 of months 3, 6, and 12.
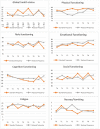
Outcome measurements and statistical analysis: Analyses were performed using an intention-to-treat analysis and a per-protocol analysis. QoL was measured using the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Quality of Life Questionnaire Core 30 version 3.0 (QLQ-C30 v.03) prior to the first and last instillations of each BCG cycle. Group differences were determined using linear regression corrected for QoL at baseline. Differences in QoL over time were tested for significance using a linear mixed model. Side effects were recorded by the treating physician using a standardized form. Chi-square tests were used to compare the side-effect frequency between the arms.
Results and limitations: There were no significant differences in the means of each QoL scale between the two arms. There were also no significant changes over time in all QoL domains for both arms. However, differences in the incidence of general malaise at T1 (before the last induction instillation), frequency, urgency, and dysuria at T7 (before the last maintenance instillation) were detected in favor of the reduced frequency arm.
Conclusions: Reducing the BCG instillation frequency does not improve the QoL in NMIBC patients despite lower storage symptoms.
Patient summary: In this study, we evaluated whether a reduction in the number of received bacillus Calmette-Guérin instillations led to better quality of life in patients with high-grade non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. We found no difference in the quality of life between the standard and the reduced bacillus Calmette-Guérin instillation frequency. We conclude that reducing the number of instillations does not lead to better quality of life in patients with high-grade non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Keywords: Bacillus Calmette-Guérin; Bladder cancer; High-grade non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer; Quality of life.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Sylvester R.J., van der Meijden A.P.M., Oosterlinck W., et al. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: a combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur Urol. 2006;49:466–477. - PubMed
-
- Mottet N., van den Bergh R.C.N., Briers E., et al. European Association of Urology guidelines. European Association of Urology; Arnhem, The Netherlands: 2021. EAU-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG guidelines on cancer 2021.
-
- Böhle A., Bock P.R. Intravesical bacille Calmette-Guérin versus mitomycin C in superficial bladder cancer: formal meta-analysis of comparative studies on tumor progression. Urology. 2004;63:682–686. - PubMed
-
- Böhle A., Jocham D., Bock P.R. Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin versus mitomycin C for superficial bladder cancer: a formal meta-analysis of comparative studies on recurrence and toxicity. J Urol. 2003;169:90–95. - PubMed

