Hyperbaric oxygen therapy as a complementary treatment in neuroblastoma - a narrative review
- PMID: 37823059
- PMCID: PMC10562625
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1254322
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy as a complementary treatment in neuroblastoma - a narrative review
Abstract
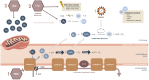
Neuroblastoma is the most frequently diagnosed cancer during the first year of life. This neoplasm originates from neural crest cells derived from the sympathetic nervous system, adrenal medulla, or paraspinal ganglia. The clinical presentation can vary from an asymptomatic mass to symptoms resulting from local invasion and/or spread of distant disease spread. The natural history of neuroblastoma is highly variable, ranging from relatively indolent biological behavior to a high-risk clinical phenotype with a dismal prognosis. Age, stage, and biological features are important prognostic risk stratification and treatment assignment prognostic factors. The multimodal therapy approach includes myeloablative chemotherapy, radiotherapy, immunotherapy, and aggressive surgical resection. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) has been proposed as a complementary measure to overcome tumor hypoxia, which is considered one of the hallmarks of this cancer treatment resistance. This article aims to review the relevant literature on the neuroblastoma pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and different biological and genetic profiles, and to discuss its management, focusing on HBOT.
Keywords: hyperbaric oxygen therapy; hyperbaric oxygenation; iodine radioisotopes; iodine-131; neuroblastoma; radiopharmaceuticals; therapy; treatment.
Copyright © 2023 Alpuim Costa, Gonçalves-Nobre, Sampaio-Alves, Guerra, Arana Ribeiro and Espiney Amaro.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

