Synergistic Combinations of Gut- and Pancreas-Hormone-Based Therapies: Advancements in Treatments for Metabolic Diseases
- PMID: 37823483
- PMCID: PMC10612476
- DOI: 10.1210/endocr/bqad153
Synergistic Combinations of Gut- and Pancreas-Hormone-Based Therapies: Advancements in Treatments for Metabolic Diseases
Abstract
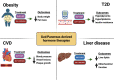
Metabolic diseases, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), cardiovascular disease, and liver disease, have become increasingly prevalent around the world. As an alternative to bariatric surgery, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists have been at the forefront of weight loss medication to combat these metabolic complications. Recently, there has been an exciting rapid emergence of new weight loss medications that combine GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists with other gut- and pancreatic-derived hormones, such as glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon (GCG) receptor agonists. Dual-agonist (GLP-1/GIP and GLP-1/GCG) and tri-agonist (GLP-1/GIP/GCG) administration generally result in greater weight loss, reduction of blood sugar and lipid levels, restoration of tissue function, and improvement in whole-body substrate metabolism compared to when GLP-1R agonists are used alone. The aim of this review is to summarize the recent literature of both preclinical and clinical studies on how these emerging gut-peptide therapies further improve weight loss and metabolic health outcomes for various metabolic diseases.
Keywords: glucagon; glucagon-like peptide-1; glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide; obesity; type 2 diabetes mellitus; weight loss.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
Paradigm Shift in the Management of Metabolic Diseases-Next-Generation Incretin Therapy.Endocrinology. 2023 Nov 2;164(12):bqad166. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqad166. Endocrinology. 2023. PMID: 37951841
References
-
- Chew NWS, Ng CH, Tan DJH, et al. . The global burden of metabolic disease: data from 2000 to 2019. Cell Metab. 2023;35(3):414‐428.e3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

