Comparison of contemporary invasive and non-invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates reveals new insights into circulating anti-microbial resistance determinants
- PMID: 37823632
- PMCID: PMC10649040
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.00785-23
Comparison of contemporary invasive and non-invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates reveals new insights into circulating anti-microbial resistance determinants
Abstract
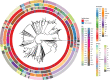
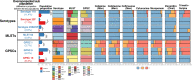
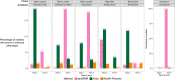
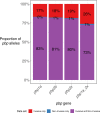
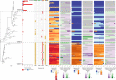
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a major human pathogen with a high burden of disease. Non-invasive isolates (those found in non-sterile sites) are thought to be a key source of invasive isolates (those found in sterile sites) and a reservoir of anti-microbial resistance (AMR) determinants. Despite this, pneumococcal surveillance has almost exclusively focused on invasive isolates. We aimed to compare contemporaneous invasive and non-invasive isolate populations to understand how they interact and identify differences in AMR gene distribution. We used a combination of whole-genome sequencing and phenotypic anti-microbial susceptibility testing and a data set of invasive (n = 1,288) and non-invasive (n = 186) pneumococcal isolates, collected in Victoria, Australia, between 2018 and 2022. The non-invasive population had increased levels of antibiotic resistance to multiple classes of antibiotics including beta-lactam antibiotics penicillin and ceftriaxone. We identified genomic intersections between the invasive and non-invasive populations and no distinct phylogenetic clustering of the two populations. However, this analysis revealed sub-populations overrepresented in each population. The sub-populations that had high levels of AMR were overrepresented in the non-invasive population. We determined that WamR-Pneumo was the most accurate in silico tool for predicting resistance to the antibiotics tested. This tool was then used to assess the allelic diversity of the penicillin-binding protein genes, which acquire mutations leading to beta-lactam antibiotic resistance, and found that they were highly conserved (≥80% shared) between the two populations. These findings show the potential of non-invasive isolates to serve as reservoirs of AMR determinants.
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumoniae; antibiotic resistance; genomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gottlieb T, Collignon PJ, Robson JM, Pearson JC, Bell JM, Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance . 2008. Prevalence of antimicrobial resistances in Streptococcus pneumoniae in Australia, 2005: report from the Australian group on antimicrobial resistance. Commun Dis Intell Q Rep 32:242–249. - PubMed
-
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. AURA 2021 Fourth Australian report on antimicrobial use and resistance in human health [Internet] . 2021. Available from: https://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/our-work/antimicrobial-resistance/an...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

