Transcriptomic cytoarchitecture reveals principles of human neocortex organization
- PMID: 37824655
- PMCID: PMC11687949
- DOI: 10.1126/science.adf6812
Transcriptomic cytoarchitecture reveals principles of human neocortex organization
Abstract
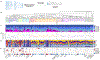
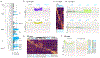
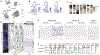
Variation in cytoarchitecture is the basis for the histological definition of cortical areas. We used single cell transcriptomics and performed cellular characterization of the human cortex to better understand cortical areal specialization. Single-nucleus RNA-sequencing of 8 areas spanning cortical structural variation showed a highly consistent cellular makeup for 24 cell subclasses. However, proportions of excitatory neuron subclasses varied substantially, likely reflecting differences in connectivity across primary sensorimotor and association cortices. Laminar organization of astrocytes and oligodendrocytes also differed across areas. Primary visual cortex showed characteristic organization with major changes in the excitatory to inhibitory neuron ratio, expansion of layer 4 excitatory neurons, and specialized inhibitory neurons. These results lay the groundwork for a refined cellular and molecular characterization of human cortical cytoarchitecture and areal specialization.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- von Economo C, Koskinas GN, Triarhou LC, Atlas of cytoarchitectonics of the adult human cerebral cortex (Karger, Basil; ; New York, 1st English ed., 2008).
-
- von Economo C, Koskinas GN, Die Cytoarchitektonik der Hirnrinde des erwachsenen Menschen.
-
- Brodmann K, Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Grosshirnrinde: in ihren Prinzipien dargestellt auf Grund d. Zellenbaues (Barth, Leipzig, Repr. d. 1. Aufl. von 1909., 1985).
-
- Vogt C, Vogt O, Allgemeine Ergebnisse unserer Hirnforschung (J.A. Barth, 1919).
-
- Amunts K, Zilles K, Architectonic Mapping of the Human Brain beyond Brodmann. Neuron. 88, 1086–1107 (2015). - PubMed

