Antimicrobial susceptibility of Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum: an in-vitro study
- PMID: 37827185
- PMCID: PMC10686905
- DOI: 10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00219-7
Antimicrobial susceptibility of Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum: an in-vitro study
Abstract
Background: The increasing incidence of syphilis and the limitations of first-line treatment with penicillin, particularly in neurosyphilis, neonatal syphilis, and pregnancy, highlight the need to expand the therapeutic repertoire for effective management of this disease. We assessed the in-vitro efficacy of 18 antibiotics from several classes on Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum (T pallidum), the syphilis bacteria.
Methods: Using the in-vitro culture system for T pallidum, we exposed the pathogen to a concentration range of each tested antibiotic. After a 7-day incubation, the treponemal burden was evaluated by quantitative PCR targeting the T pallidum tp0574 gene. The primary outcome was the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) at which the quantitative PCR values were not significantly higher than the inoculum wells. We also investigated the susceptibility of macrolide-resistant strains to high concentrations of azithromycin, and the possibility of developing resistance to linezolid, a proposed candidate for syphilis treatment.
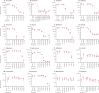
Findings: Amoxicillin, ceftriaxone, several oral cephalosporins, tedizolid, and dalbavancin exhibited anti-treponemal activity at concentrations achievable in human plasma following regular dosing regimens. The experiments revealed a MIC for amoxicillin at 0·02 mg/L, ceftriaxone at 0·0025 mg/L, cephalexin at 0·25 mg/L, cefetamet and cefixime at 0·0313 mg/L, cefuroxime at 0·0156 mg/L, tedizolid at 0·0625 mg/L, spectinomycin at 0·1 mg/L, and dalbavancin at 0·125 mg/L. The MIC for zoliflodacin and balofloxacin was 2 mg/L. Ertapenem, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and metronidazole had either a poor or no effect. Azithromycin concentrations up to 2 mg/L (64 times the MIC) were ineffective against strains carrying mutations associated to macrolide resistance. Exposure to subtherapeutic doses of linezolid for 10 weeks did not induce phenotypic or genotypic resistance.
Interpretation: Cephalosporins and oxazolidinones are potential candidates for expanding the current therapeutic repertoire for syphilis. Our findings warrant testing efficacy in animal models and, if successful, clinical assessment of efficacy.
Funding: European Research Council.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests We declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
AMR is more complicated than a lack of drugs.Lancet Microbe. 2023 Nov;4(11):e851. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00343-9. Lancet Microbe. 2023. PMID: 37924834 No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO Prevalence and incidence of selected sexually transmitted infections, Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, syphilis and Trichomonas vaginalis: methods and results used by WHO to generate 2005 estimates. 2011. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/44735
-
- Savage EJ, Hughes G, Ison C, Lowndes CM, the European Surveillance of Sexually Transmitted Infections network Syphilis and gonorrhoea in men who have sex with men: a European overview. Euro Surveill. 2009;14 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

