TRIM24-Mediated Acetylation of STAT6 Suppresses Th2-Induced Allergic Rhinitis
- PMID: 37827979
- PMCID: PMC10570786
- DOI: 10.4168/aair.2023.15.5.603
TRIM24-Mediated Acetylation of STAT6 Suppresses Th2-Induced Allergic Rhinitis
Abstract
Purpose: Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a T helper type 2 (Th2)-mediated inflammatory disease. The E3 ligase tripartite motif-containing 24 (TRIM24) regulates the recruitment of acetyltransferase CREB-binding protein (CBP) to signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6). CBP mediates the acetylation of STAT6 and decreases its activity. To date, the precise role of TRIM24 in AR has not been fully interpreted. Herein, our study aimed to explore the functions of TRIM24 in AR.
Methods: The expression of TRIM24 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and CD4+ T cells from patients with AR was measured. TRIM24-conditional knockout mice with TRIM24 deficiency in CD4+ T cells were generated. Wide-type (WT) AR mice and TRIM24-conditional knockout AR mice were established. Then, AR symptoms and interleukin (IL)-4 levels were compared. Further, the proliferation, activation and polarization of CD4+ T cells from WT mice and TRIM24 knockout mice after stimulation were determined. The effects of TRIM24 deficiency on STAT6 activities were also evaluated.
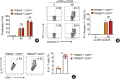
Results: Downregulated TRIM24 expression was detected in PBMCs and CD4+ T cells from patients with AR. TRIM24 conditional knockout mice had more sever AR symptoms with elevated IL-4 production. TRIM24-knockout CD4+ T cells had similar proliferation and activation when compared to WT CD4+ T cells, while they had enhanced Th2 polarization. TRIM24-knockout CD4+ T cells had decreased acetylation of STAT6 and enhanced STAT6 activities after IL-4 stimulation. The regulation of STAT6 activities by TRIM24 depended on TRIM24 N terminal RIGN domain and Lys383 acetylation site of STAT6.
Conclusions: TRIM24 suppresses Th2-mediated AR by regulating the acetylation of STAT6.
Keywords: STAT6; T cells; TRIM24; Th2; acetylation; allergic rhinitis; transcription factor.
Copyright © 2023 The Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology • The Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no financial or other issues that might lead to conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Steelant B, Seys SF, Van Gerven L, Van Woensel M, Farré R, Wawrzyniak P, et al. Histamine and T helper cytokine-driven epithelial barrier dysfunction in allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141:951–963.e8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

