Alzheimer's disease-induced phagocytic microglia express a specific profile of coding and non-coding RNAs
- PMID: 37828821
- PMCID: PMC10916983
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.13502
Alzheimer's disease-induced phagocytic microglia express a specific profile of coding and non-coding RNAs
Abstract
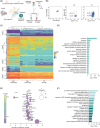
Introduction: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the main cause of dementia in the elderly. AD pathology is characterized by accumulation of microglia around the beta-amyloid (Aβ) plaques which assumes disease-specific transcriptional signatures, as for the disease-associated microglia (DAM). However, the regulators of microglial phagocytosis are still unknown.
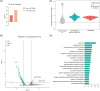
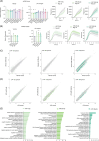
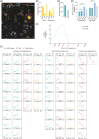
Methods: We isolated Aβ-laden microglia from the brain of 5xFAD mice for RNA sequencing to characterize the transcriptional signature in phagocytic microglia and to identify the key non-coding RNAs capable of regulating microglial phagocytosis. Through spatial sequencing, we show the transcriptional changes of microglia in the AD mouse brain in relation to Aβ proximity.
Results: Finally, we show that phagocytic messenger RNAs are regulated by miR-7a-5p, miR-29a-3p and miR-146a-5p microRNAs and segregate the DAM population into phagocytic and non-phagocytic states.
Discussion: Our study pinpoints key regulators of microglial Aβ clearing capacity suggesting new targets for future therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; microRNAs; microglia; phagocytosis; post-transcriptional regulation.
© 2023 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures


References
-
- Barker WW, Luis CA, Kashuba A, et al. Relative frequencies of Alzheimer disease, lewy body, vascular and frontotemporal dementia, and hippocampal sclerosis in the state of Florida brain bank. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2002;16:203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

