Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Misdiagnosed as Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Report of a Rare Case
- PMID: 37829961
- PMCID: PMC10565074
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.44995
Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Misdiagnosed as Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Report of a Rare Case
Abstract
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas are a diverse group of lymphoproliferative disorders rising from the lymphocytes with a broad spectrum of histological characteristics and clinical manifestations that often complicate accurate diagnosis. Autoantibodies have been observed at higher frequencies in lymphoproliferative diseases, yet the precise role of the immune system and the underlying causative factors remain enigmatic. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), an aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma variant, commonly presents in a manner akin to other aggressive lymphomas, featuring swift progression of peripheral and/or retroperitoneal adenopathy, accompanied by systemic symptoms like fever, night sweats, and weight loss. This case report delves into a histologically verified instance of ALCL, which strikingly emulates systemic lupus erythematosus. This report's objective is to underscore the concept that lymphoma can manifest clinical or biological features reminiscent of autoimmunity.
Keywords: autoimmune disorders; lymphadenopathy; misdiagnosis; multidisciplinary collaboration; non-hodgkin lymphoma; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2023, Alfroukh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
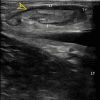
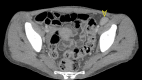
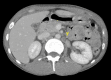
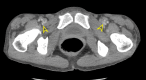
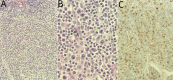
Figures

References
-
- Prevalence of factors influencing cancer risk in women with lupus: social habits, reproductive issues, and obesity. Bernatsky S, Boivin JF, Joseph L, St Pierre Y, Moore A, Rajan R, Clarke A. https://www.jrheum.org/content/29/12/2551.long. J Rheumatol. 2002;29:2551–2554. - PubMed
-
- Clinical significance of elevated antinuclear antibodies in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a single center study. Lang J, Ma K, Guo J, Zhang J, Wang Q, Sun H. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018;14:213–219. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
