Affinity membrane adsorbers for binding arginine-rich proteins
- PMID: 37830059
- PMCID: PMC10569433
- DOI: 10.1080/01496395.2016.1206934
Affinity membrane adsorbers for binding arginine-rich proteins
Abstract
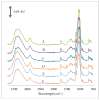
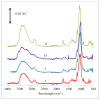
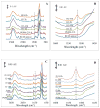
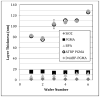
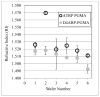
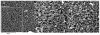
Delivering protein chemotherapeutics into cancer cells is a challenge. Fusing the protein to an arginine-rich cell-penetrating peptide offers a possible solution. The goal of this work was to develop an affinity membrane for purification of Arg-rich fusion proteins via capture chromatography. Membranes were prepared by grafting polymers bearing diethyl-4-aminobenzyl phosphonate (D4ABP) ligands from macroporous membrane supports. Incorporation of D4ABP was studied by infrared spectroscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy. Protein binding capacities of 3 mg lysozyme/mL were measured. While further studies are required to evaluate binding kinetics and Arg-selectivity, achieving higher protein binding capacity is needed before investment in such studies.
Keywords: ATRP; Arg-tag; fusion protein; membrane chromatography; surface modification.
Figures

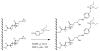
References
-
- Wang F, Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhang W, Guo S, Jin F. Recent progress of cell-penetrating peptides as new carriers for intracellular cargo delivery. J Control Release. 2014;174:126. - PubMed
-
- Beerens A, Al Hadithy A, Rots M, Haisma H. Protein transduction domains and their utility in gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther. 2003;3:486. - PubMed
-
- Green I, Christison R, Voyce CJ, Bundell KR, Lindsay MA. Protein transduction domains: are they delivering? Trends Pharmcol Sci. 2003;24:213. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y-P, Chen C-TY, Hung Y, Chou C-M, Liu T-P, Liang M-R, Chen C-T, Mou C-Y. A new strategy for intracellular delivery of enzyme using mesoporous silica nanoparticles: superoxide dismutase. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135(4):1516. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
