Clinical characteristics and prognosis of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in single-sided deafness patients
- PMID: 37830094
- PMCID: PMC10565856
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1230340
Clinical characteristics and prognosis of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in single-sided deafness patients
Abstract
Background: Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) in patients with single-sided deafness (SSD) is rare. The prognosis of the sole serviceable hearing ear is very important for these patients. However, the clinical characteristics and prognosis of SSNHL in SSD patients are not well-documented.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the clinical features and treatment outcomes of SSNHL in SSD patients.
Methods: Clinical data of 36 SSD patients and 116 non-SSD patients with unilateral SSNHL from January 2013 to December 2022 were retrospectively investigated. The clinical characteristics of the SSD patients were analyzed. All SSD patients were treated with intratympanic steroids plus intravenous steroids. Pure-tone average (PTA) and word recognition score (WRS) before and after treatment were recorded. The hearing recovery of SSNHL in SSD patients in comparison with non-SSD patients was explored. Auditory outcomes in SSD patients with different etiologies were also compared.
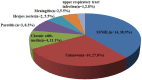
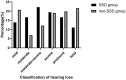
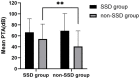
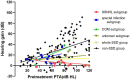
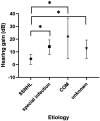
Results: Initial hearing threshold showed no significant differences between the SSD group and the non-SSD group (66.41 ± 24.64 dB HL vs. 69.21 ± 31.48 dB HL, p = 0.625). The SSD group had a higher post-treatment hearing threshold (median (interquartile range, IQR) 53.13(36.56) dB HL) than the non-SSD group (median 32.50(47.5) dB HL, p < 0.01). Hearing gains (median 8.75(13.00) dB) and the rate of significant recovery (13.89%) were lower in the SSD group than in the non-SSD group (median 23.75(34.69) dB, 45.69%). The etiology of SSD was classified as SSNHL, special types of infection, chronic otitis media, and unknown causes. SSNHL accounted for the maximum proportion (38.9%) of causes of SSD in the SSD group. Hearing gains were lower in the SSNHL-SSD group than in other causes of the SSD group. A binary logistic regression analysis demonstrated that SSD serves as an indicator of unfavorable hearing recovery outcomes (OR = 5.264, p < 0.01).
Conclusion: The prognosis of SSNHL in SSD patients is unsatisfactory. SSNHL accounts for the maximum proportion of causes of SSD in this group of patients. For SSD patients caused by SSNHL, less hearing improvement after treatment was expected when SSNHL occurred in the contralateral ear in comparison with SSD patients with other causes.
Keywords: clinical feature; glucocorticoid; prognosis; single sided deafness; sudden sensorineural hearing loss.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Wu, Li, Zhang, He, Duan and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Perez Ferreira Neto A, da Costa MR, Dore Saint Jean L, Ribeiro S, de Souza L, de Oliveira PN. Clinical profile of patients with unilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss: correlation with hearing prognosis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2021) 165:563–70. doi: 10.1177/0194599820986571, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

