Molecular basis of ClC-6 function and its impairment in human disease
- PMID: 37831762
- PMCID: PMC10575590
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adg4479
Molecular basis of ClC-6 function and its impairment in human disease
Abstract
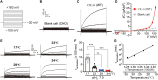
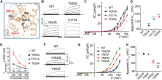
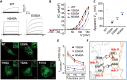
ClC-6 is a late endosomal voltage-gated chloride-proton exchanger that is predominantly expressed in the nervous system. Mutated forms of ClC-6 are associated with severe neurological disease. However, the mechanistic role of ClC-6 in normal and pathological states remains largely unknown. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of ClC-6 that guided subsequent functional studies. Previously unrecognized ATP binding to cytosolic ClC-6 domains enhanced ion transport activity. Guided by a disease-causing mutation (p.Y553C), we identified an interaction network formed by Y553/F317/T520 as potential hotspot for disease-causing mutations. This was validated by the identification of a patient with a de novo pathogenic variant p.T520A. Extending these findings, we found contacts between intramembrane helices and connecting loops that modulate the voltage dependence of ClC-6 gating and constitute additional candidate regions for disease-associated gain-of-function mutations. Besides providing insights into the structure, function, and regulation of ClC-6, our work correctly predicts hotspots for CLCN6 mutations in neurodegenerative disorders.
Figures





References
-
- T. J. Jentsch, M. Pusch, CLC chloride channels and transporters: Structure, function, physiology, and disease. Physiol. Rev. 98, 1493–1590 (2018). - PubMed
-
- G. Zifarelli, M. Pusch, CLC chloride channels and transporters: A biophysical and physiological perspective. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 158, 23–76 (2007). - PubMed
-
- M. M. Polovitskaya, C. Barbini, D. Martinelli, F. L. Harms, F. S. Cole, P. Calligari, G. Bocchinfuso, L. Stella, A. Ciolfi, M. Niceta, T. Rizza, M. Shinawi, K. Sisco, J. Johannsen, J. Denecke, R. Carrozzo, D. J. Wegner, K. Kutsche, M. Tartaglia, T. J. Jentsch, A recurrent gain-of-function mutation in CLCN6, encoding the ClC-6 Cl−/H+-exchanger, causes early-onset neurodegeneration. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 107, 1062–1077 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- T. Y. Chen, Structure and function of CLC channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 67, 809–839 (2005). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

