ADP-ribosylation from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic implications
- PMID: 37832523
- PMCID: PMC10789625
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.08.030
ADP-ribosylation from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic implications
Abstract
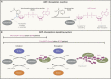
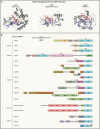
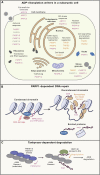
ADP-ribosylation is a ubiquitous modification of biomolecules, including proteins and nucleic acids, that regulates various cellular functions in all kingdoms of life. The recent emergence of new technologies to study ADP-ribosylation has reshaped our understanding of the molecular mechanisms that govern the establishment, removal, and recognition of this modification, as well as its impact on cellular and organismal function. These advances have also revealed the intricate involvement of ADP-ribosylation in human physiology and pathology and the enormous potential that their manipulation holds for therapy. In this review, we present the state-of-the-art findings covering the work in structural biology, biochemistry, cell biology, and clinical aspects of ADP-ribosylation.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests E.P. is an employee of Vertex Pharmaceuticals and may own stock or stock options in that company.
Figures

References
-
- Chambon P., Weill J.D., Doly J., Strosser M.T., Mandel P. On the formation of a novel adenylic compound by enzymatic extracts of liver nuclei. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1966;25:638–643.
-
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Hayaishi O. Diphtheria toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1968;243:3553–3555. - PubMed
-
- Bryant H.E., Schultz N., Thomas H.D., Parker K.M., Flower D., Lopez E., Kyle S., Meuth M., Curtin N.J., Helleday T. Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature. 2005;434:913–917. - PubMed
-
- Farmer H., McCabe N., Lord C.J., Tutt A.N.J., Johnson D.A., Richardson T.B., Santarosa M., Dillon K.J., Hickson I., Knights C., et al. Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature. 2005;434:917–921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

