Endothelial discoidin domain receptor 1 senses flow to modulate YAP activation
- PMID: 37833282
- PMCID: PMC10576099
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42341-z
Endothelial discoidin domain receptor 1 senses flow to modulate YAP activation
Abstract
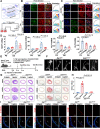
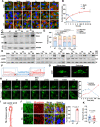
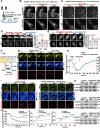
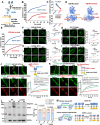
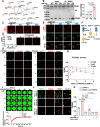
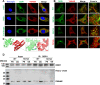
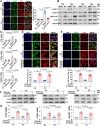
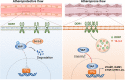
Mechanotransduction in endothelial cells is critical to maintain vascular homeostasis and can contribute to disease development, yet the molecules responsible for sensing flow remain largely unknown. Here, we demonstrate that the discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) tyrosine kinase is a direct mechanosensor and is essential for connecting the force imposed by shear to the endothelial responses. We identify the flow-induced activation of endothelial DDR1 to be atherogenic. Shear force likely causes conformational changes of DDR1 ectodomain by unfolding its DS-like domain to expose the buried cysteine-287, whose exposure facilitates force-induced receptor oligomerization and phase separation. Upon shearing, DDR1 forms liquid-like biomolecular condensates and co-condenses with YWHAE, leading to nuclear translocation of YAP. Our findings establish a previously uncharacterized role of DDR1 in directly sensing flow, propose a conceptual framework for understanding upstream regulation of the YAP signaling, and offer a mechanism by which endothelial activation of DDR1 promotes atherosclerosis.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DDR1 (Discoidin Domain Receptor-1)-RhoA (Ras Homolog Family Member A) Axis Senses Matrix Stiffness to Promote Vascular Calcification.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Jul;40(7):1763-1776. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314697. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32493168 Free PMC article.
-
Stiffness-responsive feedback autoregulation of DDR1 expression is mediated by a DDR1-YAP/TAZ axis.Matrix Biol. 2022 Jun;110:129-140. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2022.05.004. Epub 2022 May 11. Matrix Biol. 2022. PMID: 35562016
-
Diabetic Vascular Calcification Mediated by the Collagen Receptor Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 via the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Akt/Runt-Related Transcription Factor 2 Signaling Axis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Aug;38(8):1878-1889. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311238. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29930002 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling by discoidin domain receptor 1 in cancer metastasis.Cell Adh Migr. 2018;12(4):315-323. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2018.1520556. Epub 2018 Oct 13. Cell Adh Migr. 2018. PMID: 30187813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collagen recognition and transmembrane signalling by discoidin domain receptors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1834(10):2187-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.10.014. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23128141 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the relationship between hemodynamics and the immune microenvironment in carotid atherosclerosis: Insights from CFD and CyTOF technologies.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024 Oct;44(10):1733-1744. doi: 10.1177/0271678X241251976. Epub 2024 Jun 4. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024. PMID: 38833561 Free PMC article.
-
Multidimensional excavation of the current status and trends of mechanobiology in cardiovascular homeostasis and remodeling within 20 years.Mechanobiol Med. 2025 Mar 19;3(2):100127. doi: 10.1016/j.mbm.2025.100127. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mechanobiol Med. 2025. PMID: 40395770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering mechanical cues in the microenvironment: from non-malignant settings to tumor progression.Biomark Res. 2025 Jan 23;13(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40364-025-00727-9. Biomark Res. 2025. PMID: 39849659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanosensory entities and functionality of endothelial cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 23;12:1446452. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1446452. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39507419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Force-sensing protein expression in response to cardiovascular mechanotransduction.EBioMedicine. 2024 Dec;110:105412. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105412. Epub 2024 Oct 30. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39481337 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

