MST4 kinase regulates immune thrombocytopenia by phosphorylating STAT1-mediated M1 polarization of macrophages
- PMID: 37833401
- PMCID: PMC10687271
- DOI: 10.1038/s41423-023-01089-8
MST4 kinase regulates immune thrombocytopenia by phosphorylating STAT1-mediated M1 polarization of macrophages
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: MST4 kinase regulates immune thrombocytopenia by phosphorylating STAT1-mediated M1 polarization of macrophages.Cell Mol Immunol. 2023 Dec;20(12):1533. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-01094-x. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37907780 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
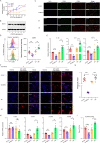
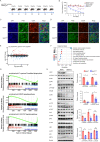
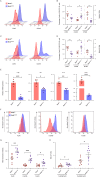
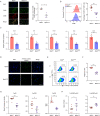
Primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an autoimmune hemorrhagic disorder in which macrophages play a critical role. Mammalian sterile-20-like kinase 4 (MST4), a member of the germinal-center kinase STE20 family, has been demonstrated to be a regulator of inflammation. Whether MST4 participates in the macrophage-dependent inflammation of ITP remains elusive. The expression and function of MST4 in macrophages of ITP patients and THP-1 cells, and of a macrophage-specific Mst4-/- (Mst4ΔM/ΔM) ITP mouse model were determined. Macrophage phagocytic assays, RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis, immunofluorescence analysis, coimmunoprecipitation (co-IP), mass spectrometry (MS), bioinformatics analysis, and phosphoproteomics analysis were performed to reveal the underlying mechanisms. The expression levels of the MST4 gene were elevated in the expanded M1-like macrophages of ITP patients, and this elevated expression of MST4 was restored to basal levels in patients with remission after high-dose dexamethasone treatment. The expression of the MST4 gene was significantly elevated in THP-1-derived M1 macrophages. Silencing of MST4 decreased the expression of M1 macrophage markers and cytokines, and impaired phagocytosis, which could be increased by overexpression of MST4. In a passive ITP mouse model, macrophage-specific depletion of Mst4 reduced the numbers of M1 macrophages in the spleen and peritoneal lavage fluid, attenuated the expression of M1 cytokines, and promoted the predominance of FcγRIIb in splenic macrophages, which resulted in amelioration of thrombocytopenia. Downregulation of MST4 directly inhibited STAT1 phosphorylation, which is essential for M1 polarization of macrophages. Our study elucidates a critical role for MST4 kinase in the pathology of ITP and identifies MST4 kinase as a potential therapeutic target for refractory ITP.
Keywords: M1 polarization; Macrophages; Mammalian sterile-20-like kinase 4 (MST4); Primary immune thrombocytopenia; Signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 (STAT1).
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to CSI and USTC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
High-dose dexamethasone or all-trans-retinoic acid restores the balance of macrophages towards M2 in immune thrombocytopenia.J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Sep;15(9):1845-1858. doi: 10.1111/jth.13767. Epub 2017 Aug 5. J Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28682499
-
ADAP restraint of STAT1 signaling regulates macrophage phagocytosis in immune thrombocytopenia.Cell Mol Immunol. 2022 Aug;19(8):898-912. doi: 10.1038/s41423-022-00881-2. Epub 2022 May 30. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35637282 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin, a key active ingredient of Jianpi Zishen Xiehuo Formula, suppresses M1 macrophage polarization and platelet phagocytosis by inhibiting STAT3 activation based on network pharmacology.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Jun;397(6):4219-4233. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02870-2. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38055068
-
Low-dose decitabine promotes M2 macrophage polarization in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia via enhancing KLF4 binding to PPARγ promoter.Clin Transl Med. 2023 Jul;13(7):e1344. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1344. Clin Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37488670 Free PMC article.
-
Itaconate derivative 4-OI inhibits M1 macrophage polarization and restores its impaired function in immune thrombocytopenia through metabolic reprogramming.Chin Med J (Engl). 2025 May 29. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003586. Online ahead of print. Chin Med J (Engl). 2025. PMID: 40437667
Cited by
-
Branched-chain amino acids supplementation induces insulin resistance and pro-inflammatory macrophage polarization via INFGR1/JAK1/STAT1 signal pathway.Mol Med. 2024 Sep 12;30(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00894-9. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39267003 Free PMC article.
-
β-Hydroxybutyrate suppresses M1 macrophage polarization through β-hydroxybutyrylation of the STAT1 protein.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Dec 3;15(12):874. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07268-3. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39627223 Free PMC article.
-
Cell death signaling and immune regulation: new perspectives on targeted therapy for sepsis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Aug 15;30(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00784-w. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40817040 Review.
-
YC-4-3, a Novel Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β Inhibitor, Alleviates the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress of Macrophages in Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 May;12(17):e2412515. doi: 10.1002/advs.202412515. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40052221 Free PMC article.
-
CDKN1A as a potential target for Eltrombopag treatment in ITP and its regulation of the communication between macrophages and transitional B cells in ITP.Ann Hematol. 2025 Jun;104(6):3183-3197. doi: 10.1007/s00277-025-06436-5. Epub 2025 Jun 14. Ann Hematol. 2025. PMID: 40515824 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

