Top caregiver concerns in Rett syndrome and related disorders: data from the US natural history study
- PMID: 37833681
- PMCID: PMC10571464
- DOI: 10.1186/s11689-023-09502-z
Top caregiver concerns in Rett syndrome and related disorders: data from the US natural history study
Abstract
Objective: Recent advances in the understanding of neurodevelopmental disorders such as Rett syndrome (RTT) have enabled the discovery of novel therapeutic approaches that require formal clinical evaluation of efficacy. Clinical trial success depends on outcome measures that assess clinical features that are most impactful for affected individuals. To determine the top concerns in RTT and RTT-related disorders we asked caregivers to list the top caregiver concerns to guide the development and selection of appropriate clinical trial outcome measures for these disorders.
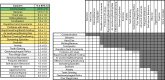
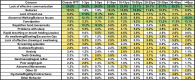
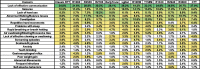
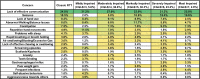
Methods: Caregivers of participants enrolled in the US Natural History Study of RTT and RTT-related disorders (n = 925) were asked to identify the top 3 concerning problems impacting the affected participant. We generated a weighted list of top caregiver concerns for each of the diagnostic categories and compared results between the disorders. Further, for classic RTT, caregiver concerns were analyzed by age, clinical severity, and common RTT-causing mutations in MECP2.
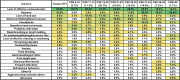
Results: The top caregiver concerns for classic RTT were effective communication, seizures, walking/balance issues, lack of hand use, and constipation. The frequency of the top caregiver concerns for classic RTT varied by age, clinical severity, and specific mutations, consistent with known variation in the frequency of clinical features across these domains. Caregivers of participants with increased seizure severity often ranked seizures as the first concern, whereas caregivers of participants without active seizures often ranked hand use or communication as the top concern. Comparison across disorders found commonalities in the top caregiver concerns between classic RTT, atypical RTT, MECP2 duplication syndrome, CDKL5 deficiency disorder, and FOXG1 syndrome; however, distinct differences in caregiver concerns between these disorders are consistent with the relative prevalence and impact of specific clinical features.
Conclusion: The top caregiver concerns for individuals with RTT and RTT-related disorders reflect the impact of the primary clinical symptoms of these disorders. This work is critical in the development of meaningful therapies, as optimal therapy should address these concerns. Further, outcome measures to be utilized in clinical trials should assess these clinical issues identified as most concerning by caregivers.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02738281.
Keywords: CDKL5; Caregiver concerns; FOXG1; MECP2 duplication; Neurodevelopmental disorders; Rett syndrome.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
JLN received research funding from the National Institutes of Health, the International Rett Syndrome Foundation, and Rett Syndrome Research Trust; clinical trials with Acadia Pharmaceuticals Inc., GW Pharmaceuticals; personal consultancy for Acadia Pharmaceuticals Inc., Analysis Group, AveXis, GW Pharmaceuticals, Hoffmann-La Roche, Myrtelle, Neurogene, Newron Pharmaceuticals, Signant Health, Taysha Gene Therapies, and the preparation of CME activities for PeerView Institute, MedEdicus, and Medscape; serves on the scientific advisory board of Alcyone Lifesciences; is a scientific cofounder of LizarBio Therapeutics; and was a member of a data safety monitoring board for clinical trials conducted by Ovid Therapeutics.
TAB received research funding from GRIN2B Foundation, International Rett Syndrome Foundation, the International Foundation for CDKL5 Research, Loulou Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, and Simons Foundation; consultancy for Alcyone, AveXis, GRIN Therapeutics, GW Pharmaceuticals, the International Rett Syndrome Foundation, Marinus Pharmaceuticals, Neurogene, Ovid Therapeutics, and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited; clinical trials with Acadia Pharmaceuticals Inc., GW Pharmaceuticals, Marinus Pharmaceuticals, Ovid Therapeutics, and Rett Syndrome Research Trust; all remuneration has been made to his department.
EDM received research support from the National Institutes of Health, Penn Orphan Disease Center, the International Rett Syndrome Foundation, Rett Syndrome Research Trust, International CDKL5 Research Foundation, and the Loulou Foundation. He has been a site principal investigator for trials from Stoke Therapeutics, Zogenix, Acadia Pharmaceuticals Inc., Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Epygenix Pharmaceuticals, and Marinus Pharmaceuticals. He has received personal compensation for consulting from Acadia Pharmaceuticals Inc. and the preparation of CME activities for Medscape.
BS has been a site investigator for clinical trials with Acadia, Marinus, and Newron; consultancy for Neurogene and Taysha; all remuneration has been paid to his department.
LS declares no competing interests.
CF has been a site investigator for clinical trials with Acadia.
SUP received research funding from the National Institutes of Health, the MECP2 Duplication Foundation, and the ActiGraph Corporation.
AKP received research funding from the National Institutes of Health, International Rett Syndrome Foundation, Rett Syndrome Research Trust; clinical trials with Acadia Pharmaceuticals Inc. and Anavex Life Sciences Corp.; and personal consultancy for Acadia Pharmaceuticals Inc. and Anavex Life Sciences Corp.
Figures

Update of
-
Top Caregiver Concerns in Rett syndrome and related disorders: data from the US Natural History Study.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 20:rs.3.rs-2566253. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2566253/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: J Neurodev Disord. 2023 Oct 13;15(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s11689-023-09502-z. PMID: 36993737 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

