Synthesis and Biological Activity of a New Indenoisoquinoline Copper Derivative as a Topoisomerase I Inhibitor
- PMID: 37834037
- PMCID: PMC10572568
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241914590
Synthesis and Biological Activity of a New Indenoisoquinoline Copper Derivative as a Topoisomerase I Inhibitor
Abstract
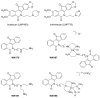
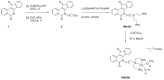
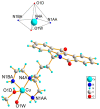
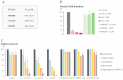
Topoisomerases are interesting targets in cancer chemotherapy. Here, we describe the design and synthesis of a novel copper(II) indenoisoquinoline complex, WN198. The new organometallic compound exhibits a cytotoxic effect on five adenocarcinoma cell lines (MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, HeLa, HT-29, and DU-145) with the lowest IC50 (0.37 ± 0.04 μM) for the triple-negative MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line. Below 5 µM, WN198 was ineffective on non-tumorigenic epithelial breast MCF-10A cells and Xenopus oocyte G2/M transition or embryonic development. Moreover, cancer cell lines showed autophagy markers including Beclin-1 accumulation and LC3-II formation. The DNA interaction of this new compound was evaluated and the dose-dependent topoisomerase I activity starting at 1 μM was confirmed using in vitro tests and has intercalation properties into DNA shown by melting curves and fluorescence measurements. Molecular modeling showed that the main interaction occurs with the aromatic ring but copper stabilizes the molecule before binding and so can putatively increase the potency as well. In this way, copper-derived indenoisoquinoline topoisomerase I inhibitor WN198 is a promising antitumorigenic agent for the development of future DNA-damaging treatments.
Keywords: DNA intercalation; adenocarcinoma; copper(II) complex; indenoisoquinoline; molecular modeling; topoisomerase I.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang P., Sadler P.J. Advances in the design of organometallic anticancer complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2017;839:5–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jorganchem.2017.03.038. - DOI
-
- Anthony E.J., Bolitho E.M., Bridgewater H.E., Carter O.W.L., Donnelly J.M., Imberti C., Lant E.C., Lermyte F., Needham R.J., Palau M., et al. Metallodrugs are unique: Opportunities and challenges of discovery and development. Chem. Sci. 2020;11:12888–12917. doi: 10.1039/D0SC04082G. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

