Synergistic Therapeutic Potential of Dual 3D Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy in an Ischemic Hind Limb Mouse Model
- PMID: 37834069
- PMCID: PMC10572732
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241914620
Synergistic Therapeutic Potential of Dual 3D Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy in an Ischemic Hind Limb Mouse Model
Abstract
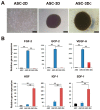
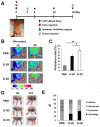
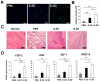
Three-dimensional (3D) culture systems have been widely used to promote the viability and metabolic activity of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). The aim of this study was to explore the synergistic benefits of using dual 3D MSC culture systems to promote vascular regeneration and enhance therapeutic potential. We used various experimental assays, including dual 3D cultures of human adipose MSCs (hASCs), quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), in vitro cell migration, Matrigel tube network formation, Matrigel plug assay, therapeutic assays using an ischemic hind limb mouse model, and immunohistochemical analysis. Our qRT-PCR results revealed that fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2), granulocyte chemotactic protein-2 (GCP-2), and vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) were highly upregulated in conventional 3D-cultured hASCs (ASC-3D) than in two-dimensional (2D)-cultured hASCs. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), and stromal-cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) showed higher expression levels in cytokine-cocktail-based, 3D-cultured hASCs (ASC-3Dc). A conditioned medium (CM) mixture of dual 3D ASCs (D-3D; ASC-3D + ASC-3Dc) resulted in higher migration and Matrigel tube formation than the CM of single 3D ASCs (S-3D; ASC-3D). Matrigel plugs containing D-3D contained more red blood cells than those containing S-3D. D-3D transplantation into ischemic mouse hind limbs prevented limb loss and augmented blood perfusion when compared to S-3D transplantation. Transplanted D-3D also revealed a high capillary density and angiogenic cytokine levels and transdifferentiated into endothelial-like cells in the hind limb muscle. These findings highlight the benefits of using the dual 3D culture system to optimize stem-cell-based therapeutic strategies, thereby advancing the therapeutic strategy for ischemic vascular disease and tissue regeneration.
Keywords: 3D culture systems; adipose mesenchymal stem cells; angiogenic potential; regenerative medicine; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Henry T.D., Annex B.H., McKendall G.R., Azrin M.A., Lopez J.J., Giordano F.J., Shah P.K., Willerson J.T., Benza R.L., Berman D.S., et al. The VIVA trial: Vascular endothelial growth factor in Ischemia for Vascular Angiogenesis. Circulation. 2003;107:1359–1365. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000061911.47710.8A. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

