Forensic Proteomics for the Discovery of New post mortem Interval Biomarkers: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 37834074
- PMCID: PMC10572818
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241914627
Forensic Proteomics for the Discovery of New post mortem Interval Biomarkers: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
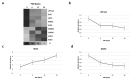
Estimating the time since death (post mortem interval, PMI) represents one of the most important tasks in daily forensic casework. For decades, forensic scientists have investigated changes in post mortem body composition, focusing on different physical, chemical, or biological aspects, to discover a reliable method for estimating PMI; nevertheless, all of these attempts remain unsuccessful considering the currently available methodical spectrum characterized by great inaccuracies and limitations. However, recent promising approaches focus on the post mortem decomposition of biomolecules. In particular, significant advances have been made in research on the post mortem degradation of proteins. In the present study, we investigated early post mortem changes (during the first 24 h) in the proteome profile of the pig skeletal muscle looking for new PMI specific biomarkers. By mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics, we were able to identify a total of nine potential PMI biomarkers, whose quantity changed constantly and progressively over time, directly or inversely proportional to the advancement of post mortem hours. Our preliminary study underlines the importance of the proteomic approach in the search for a reliable method for PMI determination and highlights the need to characterize a large number of reliable marker proteins useful in forensic practice for PMI estimation.
Keywords: biomarkers; forensic; mass spectrometry; post mortem interval (PMI); proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

