Investigating the Effects of a New Peptide, Derived from the Enterolobium contortisiliquum Proteinase Inhibitor (EcTI), on Inflammation, Remodeling, and Oxidative Stress in an Experimental Mouse Model of Asthma-Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Overlap (ACO)
- PMID: 37834157
- PMCID: PMC10573003
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241914710
Investigating the Effects of a New Peptide, Derived from the Enterolobium contortisiliquum Proteinase Inhibitor (EcTI), on Inflammation, Remodeling, and Oxidative Stress in an Experimental Mouse Model of Asthma-Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Overlap (ACO)
Abstract
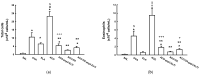
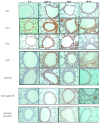
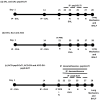
The synthesized peptide derived from Enterolobium contortisiliquum (pep3-EcTI) has been associated with potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, and it may be a potential new treatment for asthma-COPD overlap-ACO). Purpose: To investigate the primary sequence effects of pep3-EcTI in an experimental ACO. BALB/c mice were divided into eight groups: SAL (saline), OVA (ovalbumin), ELA (elastase), ACO (ovalbumin + elastase), ACO-pep3-EcTI (treated with inhibitor), ACO-DX (treated with dexamethasone), ACO-DX-pep3-EcTI (treated with dexamethasone and inhibitor), and SAL-pep3-EcTI (saline group treated with inhibitor). We evaluated the hyperresponsiveness to methacholine, exhaled nitric oxide, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), mean linear intercept (Lm), inflammatory markers, tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), interferon (IFN)), matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), growth factor (TGF-β), collagen fibers, the oxidative stress marker inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), transcription factors, and the signaling pathway NF-κB in the airways (AW) and alveolar septa (AS). Statistical analysis was conducted using one-way ANOVA and t-tests, significant when p < 0.05. ACO caused alterations in the airways and alveolar septa. Compared with SAL, ACO-pep3-EcTI reversed the changes in the percentage of resistance of the respiratory system (%Rrs), the elastance of the respiratory system (%Ers), tissue resistance (%Gtis), tissue elastance (%Htis), airway resistance (%Raw), Lm, exhaled nitric oxide (ENO), lymphocytes, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, IL-13, IL-17, TNF-α, INF-γ, MMP-12, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, collagen fibers, and iNOS. ACO-DX reversed the changes in %Rrs, %Ers, %Gtis, %Htis, %Raw, total cells, eosinophils, neutrophils, lymphocytes, macrophages, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, IL-13, IL-17, TNF-α, INF-γ, MMP-12, TGF-β, collagen fibers, and iNOS. ACO-DX-pep3-EcTI reversed the changes, as was also observed for the pep3-EcTI and the ACO-DX-pep3-EcTI. Significance: The pep3-EcTI was revealed to be a promising strategy for the treatment of ACO, asthma, and COPD.
Keywords: airway remodeling; asthma–chronic obstructive pulmonary disease overlap; inflammation; oxidative stress; protease inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. [(accessed on 15 July 2023)]. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/gina-reports/
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Global Strategy for Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (2023 Report) [(accessed on 20 May 2023)]. Available online: https://goldcopd.org/2023-gold-report-2/
-
- Soler-Cataluña J.J., Novella L., Soler C., Nieto M.L., Esteban V., Sánchez-Toril F., Miravitlles M. Clinical Characteristics and Risk of Exacerbations Associated with Different Diagnostic Criteria of Asthma-COPD Overlap. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2020;56:282–290. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2019.08.023. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

