The MADF-BESS Protein CP60 Is Recruited to Insulators via CP190 and Has Redundant Functions in Drosophila
- PMID: 37834476
- PMCID: PMC10573801
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241915029
The MADF-BESS Protein CP60 Is Recruited to Insulators via CP190 and Has Redundant Functions in Drosophila
Abstract
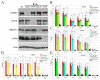
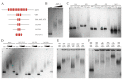
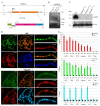
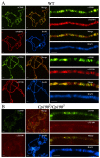
Drosophila CP190 and CP60 are transcription factors that are associated with centrosomes during mitosis. CP190 is an essential transcription factor and preferentially binds to housekeeping gene promoters and insulators through interactions with architectural proteins, including Su(Hw) and dCTCF. CP60 belongs to a family of transcription factors that contain the N-terminal MADF domain and the C-terminal BESS domain, which is characterized by the ability to homodimerize. In this study, we show that the conserved CP60 region adjacent to MADF is responsible for interacting with CP190. In contrast to the well-characterized MADF-BESS transcriptional activator Adf-1, CP60 is recruited to most chromatin sites through its interaction with CP190, and the MADF domain is likely involved in protein-protein interactions but not in DNA binding. The deletion of the Map60 gene showed that CP60 is not an essential protein, despite the strong and ubiquitous expression of CP60 at all stages of Drosophila development. Although CP60 is a stable component of the Su(Hw) insulator complex, the inactivation of CP60 does not affect the enhancer-blocking activity of the Su(Hw)-dependent gypsy insulator. Overall, our results indicate that CP60 has an important but redundant function in transcriptional regulation as a partner of the CP190 protein.
Keywords: MADF-BESS transcriptional factors; Su(Hw); architectural C2H2 proteins; gypsy; housekeeping genes; insulator.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
New Drosophila promoter-associated architectural protein Mzfp1 interacts with CP190 and is required for housekeeping gene expression and insulator activity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jul 8;52(12):6886-6905. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae393. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38769058 Free PMC article.
-
The N-Terminal Part of Drosophila CP190 Is a Platform for Interaction with Multiple Architectural Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 2;24(21):15917. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115917. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958900 Free PMC article.
-
EAST Organizes Drosophila Insulator Proteins in the Interchromosomal Nuclear Compartment and Modulates CP190 Binding to Chromatin.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 21;10(10):e0140991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140991. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26489095 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and functional role of the interaction between CP190 and the architectural protein Pita in Drosophila melanogaster.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2021 Mar 22;14(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13072-021-00391-x. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2021. PMID: 33752739 Free PMC article.
-
Functional sub-division of the Drosophila genome via chromatin looping: the emerging importance of CP190.Nucleus. 2013 Mar-Apr;4(2):115-22. doi: 10.4161/nucl.23389. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Nucleus. 2013. PMID: 23333867 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developmental and Housekeeping Genes: Two Types of Genetic Organization in the Drosophila Genome.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 6;25(7):4068. doi: 10.3390/ijms25074068. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a New Model System to Study Long-Distance Interactions Supported by Architectural Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 23;25(9):4617. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094617. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731837 Free PMC article.
-
PIF/harbinger transposon-derived protein promotes 7SL expression to enhance pathogen resistance.EMBO Rep. 2025 Mar;26(5):1196-1211. doi: 10.1038/s44319-025-00379-8. Epub 2025 Jan 30. EMBO Rep. 2025. PMID: 39885293 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

