The Evolution of Neo-Adjuvant Therapy in the Treatment of Oesophageal and Gastro-Oesophageal Junction Adenocarcinomas
- PMID: 37835435
- PMCID: PMC10571977
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15194741
The Evolution of Neo-Adjuvant Therapy in the Treatment of Oesophageal and Gastro-Oesophageal Junction Adenocarcinomas
Abstract
Historically, oesophageal and gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinomas were associated with a poor prognosis. The advent of neoadjuvant therapy has transformed the management of oesophageal and gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinomas further and offers the possibility to reverse disease progression, eliminate micrometastasis, and offer potentially better outcomes for these patients. This review provides an overview of landmark clinical trials in this area, with different treatment regimens considered over the years as well as potential therapeutic agents on the horizon that may transform the management of oesophageal and gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinomas further.
Keywords: adenocarcinoma; chemotherapy; gastro-oesophageal junction; immunotherapy; neoadjuvant; oesophagus; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
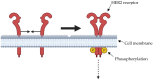
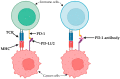

References
-
- Mukkamalla S.K.R., Recio-Boiles A., Babiker H.M. Esophageal Cancer. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2023. [(accessed on 25 April 2023)]. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459267/ - PubMed
-
- Shapiro J., van Lanschot J., Hulshof M., van Hagen P., van Berge Henegouwen M., Wijnhoven B.P.L., van Laarhoven H.W.M., Nieuwenhuijzen G.A.P., Hospers G.A.P., Bonenkamp J.J., et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery versus surgery alone for oesophageal or junctional cancer (CROSS): Long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:1090–1098. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00040-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

