A Comparison of Oocyte Yield between Ultrasound-Guided and Laparoscopic Oocyte Retrieval in Rhesus Macaques
- PMID: 37835623
- PMCID: PMC10571779
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13193017
A Comparison of Oocyte Yield between Ultrasound-Guided and Laparoscopic Oocyte Retrieval in Rhesus Macaques
Abstract
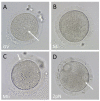
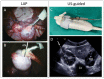
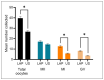
Obtaining quality oocytes is a prerequisite for ART-based studies. Here we describe a method for transabdominal ultrasound-guided (US) oocyte retrieval in rhesus macaques (Macaca mullata) and compare it to the standard surgical approach using laparoscopy (LAP). We analyzed oocyte yield from six continuous reproductive seasons (2017-2023) that included n = 177 US-guided and n = 136 laparoscopic oocyte retrievals. While the ultrasound-guided technique retrieved significantly fewer oocytes on average (LAP: 40 ± 2 vs. US: 27 ± 1), there was no difference in the number of mature metaphase II oocytes (MII) between the two techniques (LAP: 17 ± 1 vs. US: 15 ± 1). We show that oocytes retrieved by the ultrasound-guided approach fertilize at the same rates as those obtained via the laparoscopic procedure (LAP Fert Rate: 84% ± 2% vs. US Fert Rate: 83% ± 2%). In conclusion, minimally invasive ultrasound-guided oocyte retrieval improves animal welfare while delivering equivalent numbers of mature oocytes, which are ideal for ART. Furthermore, we show that oocyte competency, as represented by fertilization rate, is not affected by retrieval technique. Therefore, the Oregon National Primate Research Center (ONPRC) has adopted the ultrasound-guided approach as the standard technique for oocyte retrieval.
Keywords: animal welfare; assisted reproductive technology; laparoscopy; non-human primate; oocyte retrieval; ultrasound-guided.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study, in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Ryu J., Statz J.P., Chan W., Burch F.C., Brigande J.V., Kempton B., Porsov E.V., Renner L., McGill T., Burwitz B.J., et al. CRISPR/Cas9 Editing of the MYO7A Gene in Rhesus Macaque Embryos to Generate a Primate Model of Usher Syndrome Type 1B. Sci. Rep. 2022;12:1–13. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13689-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

