Enhancing Centelloside Production in Centella asiatica Hairy Root Lines through Metabolic Engineering of Triterpene Biosynthetic Pathway Early Genes
- PMID: 37836103
- PMCID: PMC10574710
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12193363
Enhancing Centelloside Production in Centella asiatica Hairy Root Lines through Metabolic Engineering of Triterpene Biosynthetic Pathway Early Genes
Abstract
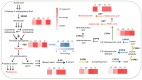
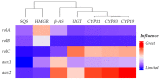
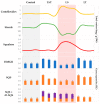
Centella asiatica is a medicinal plant with a rich tradition of use for its therapeutic properties. Among its bioactive compounds are centellosides, a group of triterpenoid secondary metabolites whose potent pharmacological activities have attracted significant attention. Metabolic engineering has emerged as a powerful biotechnological tool to enhance the production of target compounds. In this study, we explored the effects of overexpressing the squalene synthase (SQS) gene and transcription factor TSAR2 on various aspects of C. asiatica hairy root lines: the expression level of centelloside biosynthetic genes, morphological traits, as well as squalene, phytosterol, and centelloside content. Three distinct categories of transformed lines were obtained: LS, harboring At-SQS; LT, overexpressing TSAR2; and LST, simultaneously carrying both transgenes. These lines displayed noticeable alterations in morphological traits, including changes in branching rate and biomass production. Furthermore, we observed that the expression of T-DNA genes, particularly aux2 and rolC genes, significantly modulated the expression of pivotal genes involved in centelloside biosynthesis. Notably, the LS lines boasted an elevated centelloside content but concurrently displayed reduced phytosterol content, a finding that underscores the intriguing antagonistic relationship between phytosterol and triterpene pathways. Additionally, the inverse correlation between the centelloside content and morphological growth values observed in LS lines was countered by the action of TSAR2 in the LST and LT lines. This difference could be attributed to the simultaneous increase in the phytosterol content in the TSAR2-expressing lines, as these compounds are closely linked to root development. Overall, these discoveries offer valuable information for the biotechnological application of C. asiatica hairy roots and their potential to increase centelloside production.
Keywords: centelloside; machine learning; metabolic engineering; plant biotechnology; synthetic biology; triterpene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
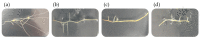

Similar articles
-
Harnessing postharvest light emitting diode (LED) technology of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. to improve centelloside content by up-regulating gene expressions in the triterpenoid pathway.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 17;10(1):e23639. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23639. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38192854 Free PMC article.
-
Using machine learning to link the influence of transferred Agrobacterium rhizogenes genes to the hormone profile and morphological traits in Centella asiatica hairy roots.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 2;13:1001023. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1001023. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36119596 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into enhancing Centella asiatica organ cell biofactories via hairy root protein profiling.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Oct 30;14:1274767. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1274767. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37965024 Free PMC article.
-
Biotechnological Intervention and Secondary Metabolite Production in Centella asiatica L.Plants (Basel). 2022 Oct 30;11(21):2928. doi: 10.3390/plants11212928. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36365380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biotechnological and endophytic-mediated production of centellosides in Centella asiatica.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Feb;107(2-3):473-489. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12316-z. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36481800 Review.
Cited by
-
Secondary Metabolites in Plants.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jul 11;14(14):2146. doi: 10.3390/plants14142146. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40733382 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic Characterization and Bioinformatic Studies of Bioactive Compounds in Two Varieties of Psidium guajava L. Leaf by GC-MS Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 12;26(6):2530. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062530. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sabaragamuwa R., Perera C.O., Fedrizzi B. Centella asiatica (Gotu Kola) as a neuroprotectant and its potential role in healthy ageing. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018;79:88–97. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2018.07.024. - DOI
-
- Kunjumon R., Johnson A.J., Baby S. Centella asiatica: Secondary Metabolites, biological activities and biomass sources. Phytomed. Plus. 2022;2:100176. doi: 10.1016/j.phyplu.2021.100176. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

