Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Restored the Saline-Alkali Soil and Promoted the Growth of Peanut Roots
- PMID: 37836166
- PMCID: PMC10574790
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12193426
Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Restored the Saline-Alkali Soil and Promoted the Growth of Peanut Roots
Abstract
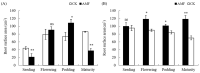
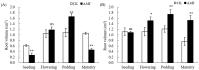
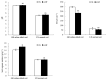
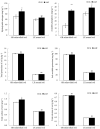
Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) is an important oil and cash crop. An efficient utilization of saline-alkali soil resources, the development of peanut planting in saline-alkali soil, and obtaining high and stable yield have become urgent needs to ensure peanut production. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) have been reported to develop the potential productivity of host plants and improve their salt resistance and tolerance. However, there is still limited research on promoting the growth and morphology of peanut roots. Therefore, in this study, seeds of salt-tolerant peanut variety "HY 25" were coated with commercial AMF inoculant before being planted in saline-alkali and normal soils to investigate the effects of AMF on peanut root growth and rhizosphere soil. The results showed that root morphological characteristics were significantly increased by the use of AMF at the podding stage in saline-alkali soil and from the flowering and pegging stage to the maturity stage in normal soil. Of note, the total root volume of peanut inoculated with AMF significantly increased by 31.57% during the podding stage in saline-alkali soil. Meanwhile, AMF significantly increased the phosphatase and invertase activities in the peanut rhizosphere of saline-alkali soil from the flowering stage to maturity stage and soil CAT activity at the maturity stage (41.16~48.82%). In normal soil, soil phosphatase and urease activities were enhanced by AMF at the flowering stage and the podding stage, respectively. AMF also increased the contents of soil organic matter, available phosphorus, and hydrolysable nitrogen, but decreased soil EC in saline-alkali soil. In addition to the significant increase in soil available phosphorus content, AMF had no significant effect on the physical and chemical properties of the soil and other soil nutrients in normal soil. AMF significantly increased pod biomass and yield in saline-alkali soil and normal soil, and improved their agronomic characteristics. In conclusion, peanut seeds coated with AMF improved the root morphological characteristics of peanuts and improved the physical and chemical properties in peanut rhizosphere, especially in saline-alkali soil. The process of rhizosphere soil nutrient transformation was also enhanced. Finally, AMF improved plant agronomic traits to increase the pod yield (16.5~21.9%). This study provides the theoretical basis and technical support for the application of AMF in peanut production in saline-alkali soil.
Keywords: arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi; peanuts; saline–alkali soil; soil enzyme activity; soil nutrient.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Abrol I.P., Yadav J.S.P., Massoud F.I. Salt-Affected Soils and Their Management. Volume 39. Food & Agriculture Org.; Rome, Italy: 1988. pp. 1–93.
-
- Zhang Z.M., Dai L.X., Ci D.W., Yang J.S., Ding H., Qin F.F., Mu G.J. Effects of planting density and sowing method on growth, development, yield and quality of peanut in saline alkali land. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2016;11:1328–1338.
-
- Nakmee P.S., Techapinyawat S., Ngamprasit S. Comparative potentials of native arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to improve nutrient uptake and biomass of Sorghum bicolor Linn. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2016;50:173–178. doi: 10.1016/j.anres.2016.06.004. - DOI
Grants and funding
- National Natural Science Foundation(31771732)/Dunwei CI
- Shandong Natural Science Foundation Youth Program (ZR2021QC163)/Dunwei CI
- Innovation Project of Agricultural science of Shandong Province (CXGC2023A46)/Feifei Qin
- Taishan Scholars Program/Jialei Zhang
- Key R&D Program of Shandong Province, China (2022CXPT031)/Jialei Zhang
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

