Sambucus nigra L. (fam. Viburnaceae) in Sicily: Distribution, Ecology, Traditional Use and Therapeutic Properties
- PMID: 37836198
- PMCID: PMC10575429
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12193457
Sambucus nigra L. (fam. Viburnaceae) in Sicily: Distribution, Ecology, Traditional Use and Therapeutic Properties
Abstract
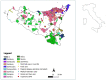
Sambucus nigra, the elderberry, has long been used for its medicinal properties in treating numerous diseases. Based on this traditional knowledge, its different pharmacological activities have been the focus of active research. All parts of the tree have long been used in traditional medicine, that is, the bark, the leaves, the flowers and the fruit. This study, carried out in Sicily (Italy), concerns the traditional uses of elder against human diseases. In order to trace the history of man's interaction with elder on the island, multidisciplinary research was carried out, aiming at (1) presenting a comprehensive overview of elderberry's applications and activities and (2) bridging traditional knowledge (uses and beliefs) with modern science, i.e., the most recent scientific findings in the biomedical and pharmacological fields. A rigorous literature review of scientific (and other local) reports on the elderberry tree and its application in food, health and household applications was undertaken. This article also provides a synthetic and updated picture of the ecology and distribution of S. nigra in Sicily. The elderberry is quite widespread in Sicily, yet its distribution is discontinuous. It prefers hedges, riparian woodlands, forest margins and clearings and is rather common along the watercourses flowing in the canyons of the Hyblaean Plateau, in the Madonie Mts. and in Enna province. Indeed, many old plants are often found near sacred places and rural houses, suggesting that in the past, it was extensively planted on purpose for its multiple uses. The complementary data obtained from multidisciplinary research confirm the usefulness of this approach in building a comprehensive and correct picture of the distribution of the most common woody species, for which the available knowledge is often fragmentary and imprecise.
Keywords: ethnobotany; place names; plant names; riparian vegetation; shrublands; traditional medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO . World Health Organization Monographs on Selected Medicinal Plants. 2nd ed. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2001.
-
- Cadar R.L., Amuza A., Dumitras D.E., Mihai M., Pocol C.B. Analysing clusters of consumers who use medicinal and aromatic plant products. Sustainability. 2021;13:8648. doi: 10.3390/su13158648. - DOI
-
- Fatima I., Safdar N., Akhtar W., Munir A., Saqib S., Ayaz A., Bahadur S., Alrefaei A.F., Ullah F., Zaman W. Evaluation of potential inhibitory effects on acetylcholinesterase, pancreatic lipase, and cancer cell lines using raw leaves extracts of three fabaceae species. Heliyon. 2023;9:e15909. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15909. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

