Polysaccharide from Smilax glabra Roxb Mitigates Intestinal Mucosal Damage by Therapeutically Restoring the Interactions between Gut Microbiota and Innate Immune Functions
- PMID: 37836386
- PMCID: PMC10574425
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15194102
Polysaccharide from Smilax glabra Roxb Mitigates Intestinal Mucosal Damage by Therapeutically Restoring the Interactions between Gut Microbiota and Innate Immune Functions
Abstract
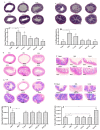
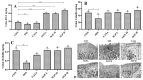
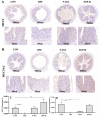
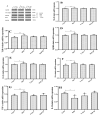
Smilax glabra Roxb (S. glabra) is a conventional Chinese medicine that is mainly used for the reliability of inflammation. However, bioactive polysaccharides from S. glabra (SGPs) have not been thoroughly investigated. Here, we demonstrate for the first time that SGPs preserve the integrity of the gut epithelial layer and protect against intestinal mucosal injury induced by dextran sulfate sodium. Mechanistically, SGPs mitigated colonic mucosal injury by restoring the association between the gut flora and innate immune functions. In particular, SGPs increased the number of goblet cells, reduced the proportion of apoptotic cells, improved the differentiation of gut tight junction proteins, and enhanced mucin production in the gut epithelial layer. Moreover, SGPs endorsed the propagation of probiotic bacteria, including Lachnospiraceae bacterium, which strongly correlated with decreased pro-inflammatory cytokines via the blocking of the TLR-4 NF-κB and MyD88 pathways. Overall, our study establishes a novel use of SGPs for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)-associated mucosal injury and provides a basis for understanding the therapeutic effects of natural polysaccharides from the perspective of symbiotic associations between host innate immune mechanisms and the gut microbiome.
Keywords: Smilax glabra Roxb polysaccharides; cytokines; goblet cells; microbiota; tight junction proteins; ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- van der Lelie D., Oka A., Taghavi S., Umeno J., Fan T.J., Merrell K.E., Watson S.D., Ouellette L., Liu B., Awoniyi M., et al. Rationally designed bacterial consortia to treat chronic immune-mediated colitis and restore intestinal homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:3105. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23460-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

