Dandelion Polysaccharides Ameliorate High-Fat-Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis in Mice through Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Capabilities
- PMID: 37836404
- PMCID: PMC10574455
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15194120
Dandelion Polysaccharides Ameliorate High-Fat-Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis in Mice through Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Capabilities
Abstract
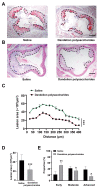
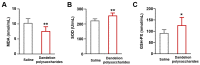
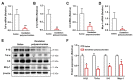
Dandelion (Taraxacum officinale), a member of the Asteraceae (Compositae) family, is well known as the traditional medical plant. Dandelion polysaccharides, a natural active ingredient extracted from the dandelion, possess immune regulation, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-aggregation properties. These properties suggest that dandelion polysaccharides might alleviate atherosclerosis. Using an ApoE-/- atherosclerotic mice model fed a high-fat diet, we investigated the impact and potential mechanism of dandelion polysaccharides on atherosclerosis. We observed that dandelion polysaccharides significantly reduced the levels of triglyceride, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol in serum, while elevated the high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol level. Concomitantly, dandelion polysaccharides reduced the area of atherosclerotic lesions and necrotic core of the aortic sinus, and increased the collagen content. Mechanistic studies showed that dandelion polysaccharides were effective in reducing serum malondialdehyde levels while elevating the enzymatic activities of superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase. Furthermore, dandelion polysaccharides reduced the expression of chemotactic factor Mcp-1 and pro-inflammatory cytokines (Tnf-α, Il-1β, and Il-6) in atherosclerotic lesions. Overall, these results indicated that dandelion polysaccharides may take an important part in the attenuation of atherosclerosis via its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; antioxidant; atherosclerosis; blood lipid profiles; dandelion polysaccharides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Anti-atherosclerosis of oligomeric proanthocyanidins from Rhodiola rosea on rat model via hypolipemic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory activities together with regulation of endothelial function.Phytomedicine. 2018 Dec 1;51:171-180. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30466614
-
Hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects of dandelion (Taraxacum officinale) root and leaf on cholesterol-fed rabbits.Int J Mol Sci. 2010 Jan 6;11(1):67-78. doi: 10.3390/ijms11010067. Int J Mol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20162002 Free PMC article.
-
Cinnamaldehyde Mitigates Atherosclerosis Induced by High-Fat Diet via Modulation of Hyperlipidemia, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jun 21;2022:4464180. doi: 10.1155/2022/4464180. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35774377 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse biological activities of dandelion.Nutr Rev. 2012 Sep;70(9):534-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2012.00509.x. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Nutr Rev. 2012. PMID: 22946853 Review.
-
The potential of dandelion in the fight against gastrointestinal diseases: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jul 15;293:115272. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115272. Epub 2022 Apr 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35405251 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Nanomaterials in Early Imaging and Advanced Treatment of Atherosclerosis.Chem Biomed Imaging. 2025 Jan 21;3(2):51-76. doi: 10.1021/cbmi.4c00064. eCollection 2025 Feb 24. Chem Biomed Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40018650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Joint exploration of network pharmacology and metabolomics on the effects of traditional Chinese medicine compounds in weaned yaks.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Jan 13;11:1511311. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1511311. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 39872609 Free PMC article.
-
Taraxacum Mongolicum Polysaccharides Reverses Mice Obesity via Activation of AKT/mTOR Pathway.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 30;16(19):3330. doi: 10.3390/nu16193330. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39408297 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of ultrasonic-assisted enzymes extraction on antioxidant polysaccharide activity in dandelion.Ultrason Sonochem. 2025 May;116:107329. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2025.107329. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Ultrason Sonochem. 2025. PMID: 40158263 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Compounds from Vegetal Organs of Taraxacum Species (Dandelion) with Biomedical Applications: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 7;26(2):450. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020450. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859166 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Virani S.S., Alonso A., Benjamin E.J., Bittencourt M.S., Callaway C.W., Carson A.P., Chamberlain A.M., Chang A.R., Cheng S., Delling F.N., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2020 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141:e139–e596. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zha X.-Q., Xiao J.-J., Zhang H.-N., Wang J.-H., Pan L.-H., Yang X.-F., Luo J.-P. Polysaccharides in Laminaria Japonica (LP): Extraction, Physicochemical Properties and Their Hypolipidemic Activities in Diet-Induced Mouse Model of Atherosclerosis. Food Chem. 2012;134:244–252. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.02.129. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

