Discovery of Novel Mono-Carbonyl Curcumin Derivatives as Potential Anti-Hepatoma Agents
- PMID: 37836639
- PMCID: PMC10574324
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28196796
Discovery of Novel Mono-Carbonyl Curcumin Derivatives as Potential Anti-Hepatoma Agents
Abstract
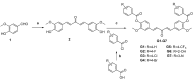
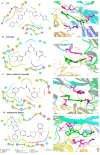
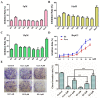
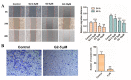
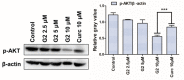
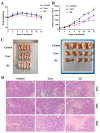
Curcumin possesses a wide spectrum of liver cancer inhibition effects, yet it has chemical instability and poor metabolic properties as a drug candidate. To alleviate these problems, a series of new mono-carbonyl curcumin derivatives G1-G7 were designed, synthesized, and evaluated by in vitro and in vivo studies. Compound G2 was found to be the most potent derivative (IC50 = 15.39 μM) compared to curcumin (IC50 = 40.56 μM) by anti-proliferation assay. Subsequently, molecular docking, wound healing, transwell, JC-1 staining, and Western blotting experiments were performed, and it was found that compound G2 could suppress cell migration and induce cell apoptosis by inhibiting the phosphorylation of AKT and affecting the expression of apoptosis-related proteins. Moreover, the HepG2 cell xenograft model and H&E staining results confirmed that compound G2 was more effective than curcumin in inhibiting tumor growth. Hence, G2 is a promising leading compound with the potential to be developed as a chemotherapy agent for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Keywords: AKT inhibition; anti-hepatoma activity; curcumin derivatives; molecular docking; xenograft model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Noorafshan A., Ashkani-Esfahani S. A review of therapeutic effects of curcumin. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013;19:2032–2046. - PubMed
-
- Ireson C.R., Jones D.J.L., Orr S., Coughtrie M.W.H., Boocock D.J., Williams M.L., Farmer P.B., Steward W.P., Gescher A.J. Metabolism of the cancer chemopreventive agent curcumin in human and rat intestine. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2002;11:105–111. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

