In Vitro Enzyme Kinetics and NMR-Based Product Elucidation for Glutathione S-Conjugation of the Anticancer Unsymmetrical Bisacridine C-2028 in Liver Microsomes and Cytosol: Major Role of Glutathione S-Transferase M1-1 Isoenzyme
- PMID: 37836655
- PMCID: PMC10574777
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28196812
In Vitro Enzyme Kinetics and NMR-Based Product Elucidation for Glutathione S-Conjugation of the Anticancer Unsymmetrical Bisacridine C-2028 in Liver Microsomes and Cytosol: Major Role of Glutathione S-Transferase M1-1 Isoenzyme
Abstract
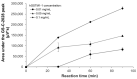
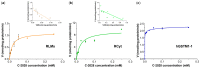
This work is the next step in studying the interplay between C-2028 (anticancer-active unsymmetrical bisacridine developed in our group) and the glutathione S-transferase/glutathione (GST/GSH) system. Here, we analyzed the concentration- and pH-dependent GSH conjugation of C-2028 in rat liver microsomes and cytosol. We also applied three recombinant human GST isoenzymes, which altered expression was found in various tumors. The formation of GSH S-conjugate of C-2028 in liver subfractions followed Michaelis-Menten kinetics. We found that C-2028 was conjugated with GSH preferentially by GSTM1-1, revealing a sigmoidal kinetic model. Using a colorimetric assay (MTT test), we initially assessed the cellular GST/GSH-dependent biotransformation of C-2028 in relation to cytotoxicity against Du-145 human prostate cancer cells in the presence or absence of the modulator of GSH biosynthesis. Pretreatment of cells with buthionine sulfoximine resulted in a cytotoxicity decrease, suggesting a possible GSH-mediated bioactivation process. Altogether, our results confirmed the importance of GSH conjugation in C-2028 metabolism, which humans must consider when planning a treatment strategy. Finally, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy elucidated the structure of the GSH-derived product of C-2028. Hence, synthesizing the compound standard necessary for further advanced biological and bioanalytical investigations will be achievable.
Keywords: GSTM; NMR-based product elucidation; anticancer unsymmetrical bisacridine; enzyme kinetics; glutathione S-conjugate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Paluszkiewicz E., Horowska B., Borowa-Mazgaj B., Peszyńska-Sularz G., Paradziej-Łukowicz J., Augustin E., Konopa J., Mazerska Z. Design synthesis and high antitumor potential of new unsymmetrical bisacridine derivatives towards human solid tumors specifically pancreatic cancers and their unique ability to stabilize DNA G-quadruplexes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020;204:11259. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112599. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pilch J., Matysiak-Brynda E., Kowalczyk A., Bujak P., Mazerska Z., Nowicka A.M., Augustin E. New unsymmetrical bisacridine derivatives noncovalently attached to quaternary quantum dots improve cancer therapy by enhancing cytotoxicity toward cancer cells and protecting normal cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2020;12:17276–17289. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c02621. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kosno M., Laskowski T., Frackowiak J.E., Potęga A., Kurdyn A., Andrałojć W., Borzyszkowska-Bukowska J., Szwarc-Karabyka K., Mazerska Z. Acid–base equilibrium and self-association in relation to high antitumor activity of selected unsymmetrical bisacridines established by extensive chemometric analysis. Molecules. 2022;27:3995. doi: 10.3390/molecules27133995. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

